SCORES & OUTDOORS: Why are all these trees dripping on me?
“Why are all these trees dripping on us,” was a question I was asked last week by a neighbor at camp. “It isn’t sap, just water.”
Well, the simple answer is that the tree is “sweating.”
Now, for the more scientific explanation.
According to the United States Geological Survey, the process is actually called transpiration, and it is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as from leaves but also from stems and flowers. Leaf surfaces are dotted with  pores, similar to our skin, which are called stomata, and in most plants they are more numerous on the undersides of the foliage. The stomata are bordered by guard cells and their accessory cells that open and close the pore. Transpiration occurs through the stomatal apertures, and can be thought of as a necessary cost associated with the opening of the stomata to allow the diffusion of carbon dioxide gas from the air for photosynthesis. Transpiration also cools plants – again similar to our sweating – changes the pressure of cells, and enables mass flow of mineral nutrients and water from roots to shoots.
pores, similar to our skin, which are called stomata, and in most plants they are more numerous on the undersides of the foliage. The stomata are bordered by guard cells and their accessory cells that open and close the pore. Transpiration occurs through the stomatal apertures, and can be thought of as a necessary cost associated with the opening of the stomata to allow the diffusion of carbon dioxide gas from the air for photosynthesis. Transpiration also cools plants – again similar to our sweating – changes the pressure of cells, and enables mass flow of mineral nutrients and water from roots to shoots.
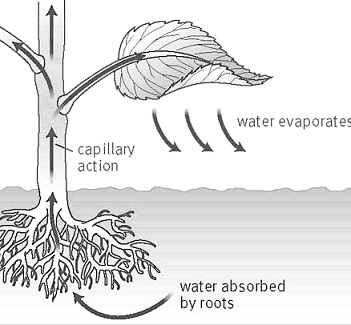
Mass flow of liquid water from the roots to the leaves is driven in part by capillary action, but primarily driven by water potential differences. In taller plants and trees, the force of gravity can only be overcome by the decrease in water pressure in the upper parts of the plants due to the diffusion of water out of stomata into the atmosphere. Water is absorbed at the roots by osmosis, and any dissolved mineral nutrients travel with it through the xylem (the woody portion of the plant).
Plant transpiration is pretty much an invisible process, since the water is evaporating from the leaf surfaces, you don’t just go out and see the leaves “sweating.” Just because you can’t see the water doesn’t mean it is not being put into the air, though. During a growing season, a leaf will transpire many times more water than its own weight. An acre of corn gives off about 3,000-4,000 gallons of water each day, and a large oak tree can transpire 40,000 gallons per year.
The rate of transpiration is also influenced by the evaporative demand of the atmosphere surrounding the leaf such as humidity, change in temperature, wind and incident sunlight.
 Soil water supply and soil temperature can influence stomatal opening, and thus transpiration rate. The amount of water lost by a plant also depends on its size and the amount of water absorbed at the roots. Transpiration accounts for most of the water loss by a plant, but some direct evaporation also takes place through the cuticle of the leaves and young stems. Transpiration serves to evaporatively cool plants as the escaping water vapor carries away heat energy.
Soil water supply and soil temperature can influence stomatal opening, and thus transpiration rate. The amount of water lost by a plant also depends on its size and the amount of water absorbed at the roots. Transpiration accounts for most of the water loss by a plant, but some direct evaporation also takes place through the cuticle of the leaves and young stems. Transpiration serves to evaporatively cool plants as the escaping water vapor carries away heat energy.
Transpiration rates go up as the temperature goes up, especially during the growing season, when the air is warmer due to stronger sunlight and warmer air masses. Higher temperatures cause the plant cells which control the openings (stoma) where water is released to the atmosphere to open, whereas colder temperatures cause the openings to close.
As the relative humidity of the air surrounding the plant rises the transpiration rate falls. It is easier for water to evaporate into dryer air than into more saturated air.
Increased movement of the air around a plant will result in a higher transpiration rate. This is somewhat related to the relative humidity of the air, in that as water transpires from a leaf, the water saturates the air surrounding the leaf. If there is no wind, the air around the leaf may not move very much, raising the humidity of the air around the leaf. Wind will move the air around, with the result that the more saturated air close to the leaf is replaced by drier air.
When moisture is lacking, plants can begin premature aging, which can result in leaf loss, and transpire less water.
So, if anyone asks you why the trees are dripping, you can go into the long, scientific explanation, or you just simply say, “the tree is sweating,” and watch for the looks you will get.
Responsible journalism is hard work!
It is also expensive!
If you enjoy reading The Town Line and the good news we bring you each week, would you consider a donation to help us continue the work we’re doing?
The Town Line is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit private foundation, and all donations are tax deductible under the Internal Revenue Service code.
To help, please visit our online donation page or mail a check payable to The Town Line, PO Box 89, South China, ME 04358. Your contribution is appreciated!


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!