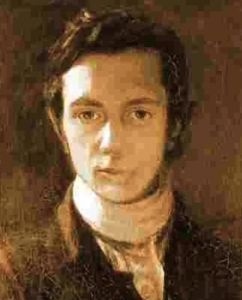REVIEW POTPOURRI: Ralph Meeker (Actor)
 by Peter Cates
by Peter Cates
Ralph Meeker
Ralph Meeker (1920-1988) was labeled perhaps a bit misleadingly as a character actor; on film and television, he did portray men on both sides of the law but he didn’t have the characterizing artistry of a Rod Steiger or Sir Lawrence Olivier.
What Meeker did have was a tough, almost explosive masculine screen presence. Examples would be the smiling rattlesnake outlaw he portrayed on the late 1950s Disney series Texas John Slaughter, the coldly focused detective in the 1955 Kiss Me Deadly who smashes a rare opera 78 in pieces to get information from a reluctant witness and the kidnapper who gets sent to prison in Big House USA, also from 1955, and escapes with four deadly cell mates, portrayed with consummate persuasion by Broderick Crawford, William Talman, Lon Chaney Jr. and Charles Bronson.
Meeker was also a motorcycle cop in the 1953 Code Two, whose slightly rebellious attitude during police basic training is pulverized by a drill instructor convincingly brought to life by actor Keenan Wynn.
The 1955 season one of Alfred Hitchcock Presents began with an episode Revenge, one of a few directed by Hitchcock himself and starring Meeker and Vera Miles as a married couple who has relocated from back East and set up temporary living quarters in a trailer park community on the otherwise still unspoiled Pacific Coast.
We find out that the wife is under doctor’s orders to take it easy for a few months after having suffered a nervous breakdown, that the husband has taken an engineering job at a nearby plant but that otherwise he does most of the cooking and other domestic chores so that his wife can relax as much as possible.
Meeker displays an endearing tenderness as the husband. As he leaves for the day, his wife promises a surprise dessert that evening.
Inevitably, Hitchcock being Hitchcock, the plot thickens. The husband returns home to find out that the wife has been violently raped (due to 1950s censorship, the word is assaulted) during a home invasion by a salesman.
Events proceed to where the couple is driving around the surrounding area, the wife sees a man walking on the street and yells, “That’s him!” The husband sneaks into the stranger’s hotel room and murders him with a wrench.
As they drive away, the – well, I won’t reveal the ending.
CSI: New York
I recently started watching the 2004 opening season of CSI: New York starring Gary Sinise as the lead investigator in the forensics unit of the Manhattan Police Department. My most memorable experiences of Sinise’s acting were in Ransom as a psychotic kidnapper and in Snake Eyes as the assassin of a Secretary of Defense . He conveyed a brutal ruthlessness in both roles.
In the TV series, Sinise started off with a strong presence but then has been getting more stiff and boring in subsequent episodes.
* * * * * *
Mozart: Magic Flute – La Dove Prende; Emma Eames, soprano and Emilio de Gogorza, baritone. Victor Red Seal 89003.
A very charmingly sung duet as sung by Eames and Gogorza who were married for over 25 years and resided much of the year in Bath, Maine.
Rossini: Stabat Mater – Cujus Animam; Evan Williams, tenor. Victor Red Seal 74093. Evan Williams sang a truly spirited performance of this very joyous aria from Rossini’s Oratorio. He passed away in 1919 from an infected boil at the age of 52. Williams, Enrico Caruso and John McCormack were considered Victor’s three most popular tenors during the World War I years.
Strauss: Blue Danube Waltz; soprano Frieda Hempel. Victor Red Seal 88540. The world’s most famous waltz gets a nice but not exactly earth shaking vocal performance.
Handel: Il Pensieroso- Sweet Bird, That Shunn’st the Noise of Folly; soprano Nellie Melba. Victor Red Seal 88068. Australian soprano Nellie Melba left many splendid shellacs and this one from a rarely heard opera of George Frederick Handel is sung with beauty and expressive dexterity.
Gluck: Orfeo and Euridice – On My Faith Relying; soprano Joanna Gadski and contralto Louise Homer. Victrola Red Seal 89041.
Both Gadski and Homer were huge successes at the Metropolitan Opera of the pre-World War I years. Gadski was most acclaimed in the operas of Mozart and Wagner while Homer sang the male role of Orfeo, as contraltos Rise Stevens and Marilyn Horne would 50 years later.
I have enjoyed their various other Victor shellacs but, strangely, this one didn’t quite get off the ground both in performance and the very dimly recorded sound.
All five of the above Red Seals came from the pre-electric microphone years and can be heard via YouTube.