Up and down the Kennebec Valley: Notable women
by Mary Grow
As background for this piece on a small selection of women of importance from the central Kennebec Valley, some historical notes might establish a useful timeline.
1) The 19th Amendment to the United States Constitution says: “The right of citizens of the United States to vote shall not be denied or abridged by the United States or by any State on account of sex.” It was passed in the House of Representatives on May 21, 1919, by a generous margin, and in the Senate on June 4, 1919, by a vote of 56 to 25, two votes more than the two-thirds majority required for a Constitutional amendment. The necessary 36th state ratification was Tennessee’s on Aug. 18, 1920.
The 89th amendment to the Maine Constitution, which prohibits discrimination on the basis of race, religion, sex or ancestry, was approved by referendum, by about a five to two margin, on Nov. 5, 1963.
2) According to an online history of the Maine Medical Association (founded in the spring of 1853 after its predecessor, the 1820 Medical Society of Maine, disbanded in 1845), in 1900 Maine had 1,206 physicians registered, of whom 67 were women. In 1982, 1,300 of 1,952 Maine practicing physicians were Association members, including 75 women.
In September 2003, the Maine Medical Association elected its first female president, Dr. Maroulla Gleaton, a Palermo resident and board-certified ophthalmologist practicing in Augusta.
3) Maine’s State Teachers Association was founded in November 1859, in Waterville. It became the Maine Education Association (MEA) in 1867 (and inherited the Teachers Association’s treasury’s assets of $1.26); in 1882 briefly merged with the 1876 Maine Teachers Association (MTA) to form the Maine Pedagogical Society; became MTA for much of the 20th century; and in 1993 became MEA again.
The initial association’s all-male founders are described on the MEA website as “superintendents, principals, college professors and teachers in large towns.” The two-thirds of Maine teachers who were women were not included until 1862. Their dues when admitted were half the men’s dues – proportional to their pay, the website comments.
In 1881, while Nelson Luce, of Vassalboro, was the State Superintendent of Schools, one of his recommendations led to state laws that for the first time allowed women to be school board members and school supervisors. The MTA’s first woman president was Helen Robinson, elected in 1927.
4) The Maine legislature created the Maine State Bar Association on March 6, 1891, to promote the legal profession and propose legal reforms. Wikipedia calls Maine’s a “relatively progressive bar,” having admitted the first recognized black lawyer in the United States, Macon Allen (who practiced briefly in Portland) in 1844. The Bar Association accepted its first woman member, Eva Bean from Old Orchard Beach, in 1911.
Against this background, it is easier to understand the importance of women who succeeded in traditionally male professions and activities in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
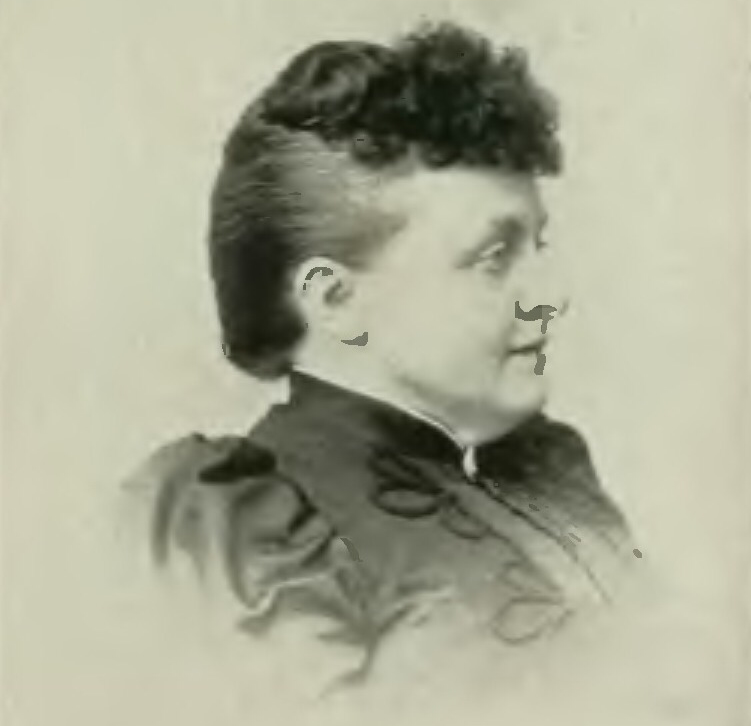
One of the employees in the Augusta-based E. C. Allen Publishing Company (see The Town Line, Nov. 12) was Woolwich native and former teacher Novella Jewell Trott (1846-1929). Joining Allen’s firm in 1881, she became an editor within two years, in charge of magazines called Practical Housekeeper and Daughters of America. An online site says she was responsible for all editing work, including reading submissions, choosing and improving material and composing her own articles. By 1894, Trott was an assistant editor for William Howard Gannett.
In 1893, Trott was one of seven women “of national reputation” who represented the Queen Isabella Association’s press department at the World’s Columbian Exposition, in Chicago, celebrating the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus’s discovery of America. A group of professional women organized the association in 1889 to honor Queen Isabella, of Spain, who financed Columbus, by commissioning a statue of her by an association member, sculptor Harriet Hosmer.
Florence Brooks Whitehouse (1869-1945) was born in Augusta and later lived in Portland. Her mother, Mary Caroline Wadsworth, was related to the family of Henry Wadsworth Longfellow; her father, Samuel Spencer Brooks, was a wealthy shipbuilder and businessman, a hardware store owner with a reputation for integrity.
Educated in Augusta schools and at a private Episcopal finishing school called St. Catherine’s Hall, Whitehouse was unusually independent for her time. Online sources say she skipped college to study fine arts in Boston for several years; visited Europe and the Middle East; and spent the winter of 1892 on a sailing barge on the Nile River with members of the McCormick family (descendants of mid-Westerners Robert and Cyrus McCormick, inventors of the McCormick reaper). While in Egypt, Kingsbury wrote, she was a newspaper correspondent.
On June 21, 1894, Florence Brooks married Robert Treat Whitehouse, also Augusta-born, son of Vassalboro native William Penn Whitehouse, who was an Associate Justice (later Chief Justice) of the Maine Supreme Court. Robert Whitehouse was a Harvard-educated lawyer who wrote several law books early in the 20th century.
The Whitehouses lived in Portland and had three sons, born between 1895 and 1904. An online source describes the marriage as “egalitarian.” Florence Whitehouse wrote two romance novels with Middle Eastern settings, The God of Things: A Novel of Modern Egypt (published in 1902) and The Effendi: A Romance of the Soudan (1904), as well as short stories and plays.
According to an online biography by historian Anne Gass and Loyola University student Robert Pirages, Whitehouse’s activity in Portland’s Civic Club showed her that if women and children were to be treated justly, women needed a greater voice in public affairs.
In 1914, Whitehouse joined the Maine Woman Suffrage Association (MWSA), whose main goal was a state equal rights amendment. She soon became a leading speaker, debater and writer for the group. Gass and Pirages wrote that she had significant family support: her father-in-law had been advocating for women’s suffrage since 1874, and in 1914 her husband helped found and chaired the Men’s Equal Suffrage League.
In 1915, frustrated by state legislators’ inaction, Whitehouse founded and, for five years, chaired the Maine branch of the Congressional Union (CU), a national organization fighting for a federal equal rights amendment. CU was considered a radical group because of its tactics, which included picketing President Woodrow Wilson’s office. Whitehouse joined out-of-state protests; in Maine, not all her fellow suffragists could support CU. In 1917 she resigned from MWSA.
Whitehouse lobbied hard to persuade Maine’s national legislators to approve and state legislators to ratify the 19th amendment. When Governor Carl Milliken called a special session of the Maine legislature on Nov. 4, 1919, to act on ratification, Whitehouse and national suffragist Alice Paul were leaders in bringing about its passage, by a four-vote margin.
The CU became the National Women’s Party in 1916, and Whitehouse remained involved. She was also active in the Portland Chamber of Commerce and increasingly in state and national anti-war movements. Supporting the League of Nations and international disarmament, she chaired international cooperation committees for the Maine League of Women Voters and the Maine Federation of Churches, represented Maine’s Peace commission on the World Unity Council and was a member of the National Council on the Prevention of War.
Whitehouse was chosen a member of the Maine Women’s Hall of Fame in 2008.
Ninetta May Runnals (1885-1980) was born in Dover-Foxcroft, but earned both her bachelor’s degree and her professional reputation at Colby College in Waterville. Graduating in Colby’s Class of 1908 with a mathematics major, she taught at Foxcroft Academy in Dover-Foxcroft for three years and was Maine Central Institute’s Dean of Girls for another five years.
When Colby trustees decided in 1916 the college needed a dean of women, President Arthur Roberts invited Runnals to apply for the job. Two sources quote from his letter: the invitation was for “the coming year and the rest of your life.”
Runnals refused, because she wanted to complete her master’s degree in mathematics at Columbia University. After she received it in 1920, she told Roberts she would accept his still-open offer, provided that the position included a professorship and that the trustees gave the dean broader responsibilities. Her conditions were approved, and in 1920 she became Colby’s Dean of Women and an Assistant Professor of Mathematics.
Runnals held the deanship for 27 years, with a break (1926-28) to work at Hillsdale College, in Hillsdale, Michigan. In 1923 she became a full professor at Colby, and after 1928 she taught education courses as well as mathematics.
Colby had begun in 1813 as a Baptist institution, but shed its religious affiliation after Maine separated from Massachusetts. The college was originally located on College Avenue, in Waterville. The present Mayflower Hill campus was acquired in 1931.
Students were all men until 1871, when Mary Caffrey Low, of Waterville, became the first and for two years only woman enrolled. She was valedictorian of the Class of 1875, which by then included five female students.
Male and female students were “resegregated” in 1890, Wikipedia says, and when Runnals became Dean of Women the trustees had plans to create a separate women’s college. Knowing the men’s college would get the bulk of resources if the separation occurred, Runnals successfully fought the proposal.
In following years she brought about other changes that improved Colby and especially enhanced women’s education. Her causes included upgrading the women’s physical education program, fighting for equal salaries for women faculty members, leading a 1930s fund drive for the women’s union building on the Mayflower Hill campus (renamed Runnals Union in 1959) and helping plan women’s dormitories in the early 1940s. In 1938, she was the first female faculty member to be honored by the senior class dedicating the college yearbook, the Colby Oracle to her “[i]n hearty appreciation of her enthusiastic participation in and cooperation with the academic, administrative, and social life of Colby.”
Runnals retired on Sept. 1, 1949. She served on the Colby Board of Trustees for six years, and remained active in college business the rest of her life, especially supporting equity for women. Colby awarded her an honorary doctorate in 1929. In 1992 she became a member of the Maine Women’s Hall of Fame.
Runnals was a founder of the Waterville branch of the American Association of University Women. In 1973 a citation from the national AAUW recognized her promotion of women’s education.
Jean Gannett Hawley (1924-1994) became executive vice-president of Guy Gannett Publishing Company in 1953 (see The Town Line, Nov. 12). An online source says it was she who changed the company name to the more inclusive Guy Gannett Communications.
Hawley was educated at Bradford Junior College (since 1971, Bradford College), in Haverhill, Massachusetts, where an online biography says she was a music major and harpist. Another website lists her four honorary doctorates, including a 1959 Doctorate of Humane Letters awarded by Colby College, on whose Board of Trustees she served from 1960 to 1972.
Her online biographer commented that her job overseeing Gannett’s newspaper chain was “made more difficult by the absence of other women in similar positions.” Nonetheless, from her base in Portland she expanded Gannett’s business in television and computers, including adding television stations in other states.
Hawley was chairman of the Gannett Board of Directors from 1959 until her death Sept. 4, 1994. Her niece, Madeleine G. Corson, who had been the board’s vice-chairman since 1990, succeeded to the chairmanship on Sept. 27, 1994.
There is no photo of Jean Gannett Hawley available.
Main sources
Kingsbury, Henry D., ed., Illustrated History of Kennebec County Maine 1625-1892 (1892).
Websites, miscellaneous.
Responsible journalism is hard work!
It is also expensive!
If you enjoy reading The Town Line and the good news we bring you each week, would you consider a donation to help us continue the work we’re doing?
The Town Line is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit private foundation, and all donations are tax deductible under the Internal Revenue Service code.
To help, please visit our online donation page or mail a check payable to The Town Line, PO Box 89, South China, ME 04358. Your contribution is appreciated!







Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!