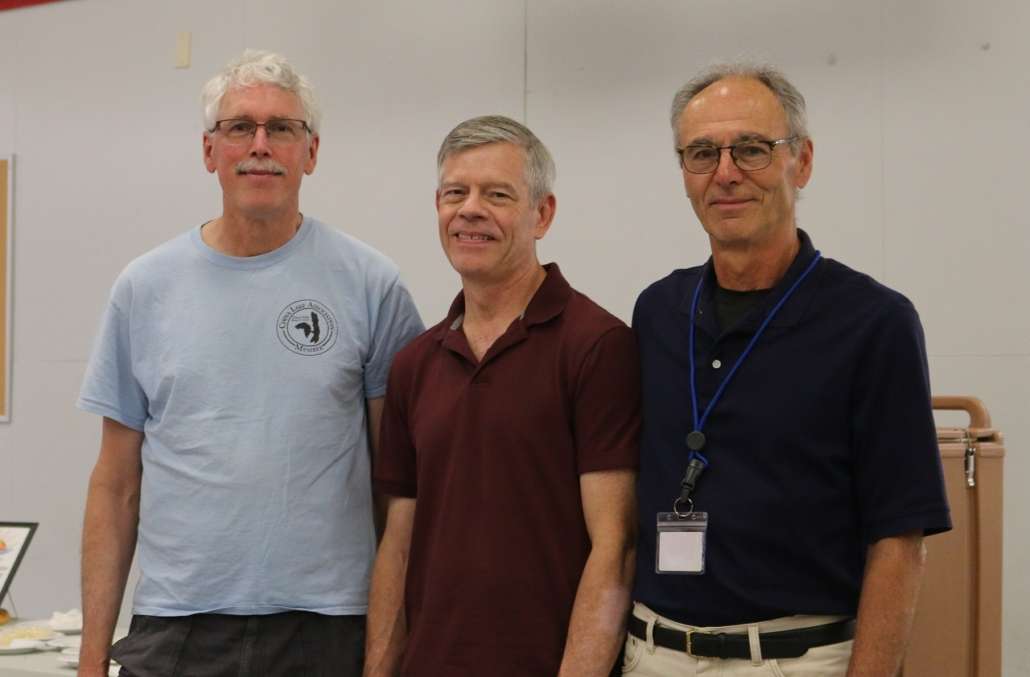
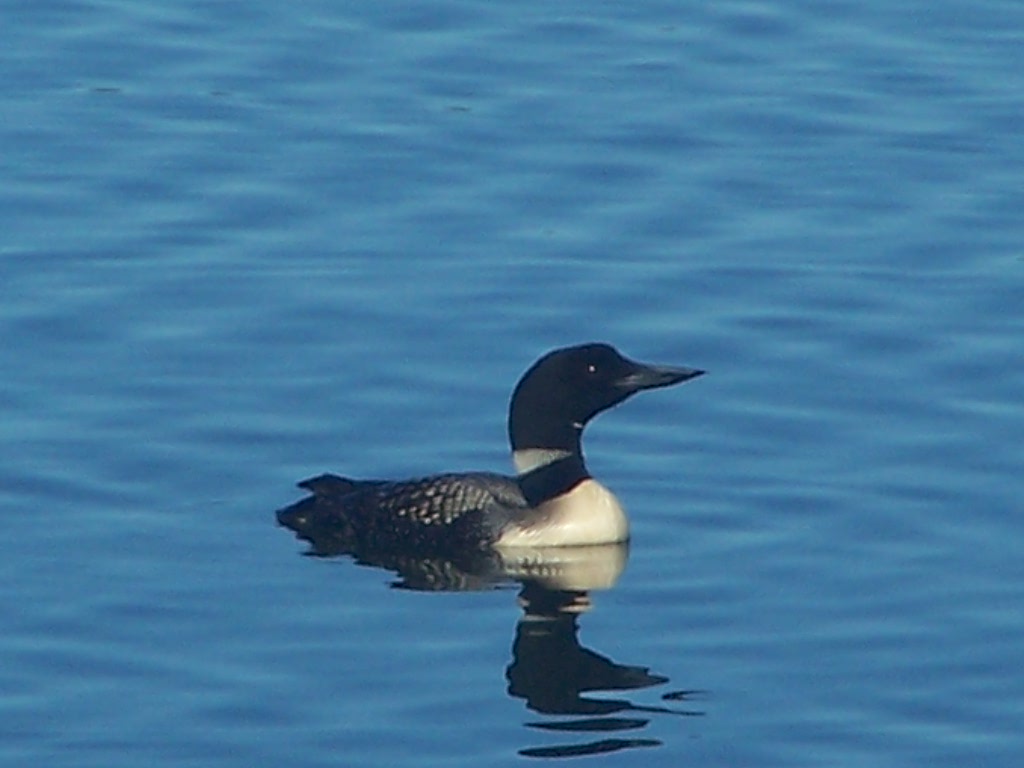
The China Lake Association leadership team, from left to right, Secretary David Preston, Vice President Eric Lind, and President Stephen Greene. (photo by Jeanne Marquis)
The China Lake Association (CLA) annual meeting was held Saturday morning on July, 30, 2022, in the China Middle School, on Lakeview Drive, in China, Maine. The meeting was both a celebration of the alewives return to China Lake and a tribute to the 50-year anniversary of the Clean Water Act.
Senator Susan Collins, Senator Angus King and Congresswoman Chellie Pingree sent video statements to the annual meeting congratulating the association’s positive impact on China Lake and supporting the work ahead to maintain the water quality. Senator Collins expressed that maintaining fresh water lakes such as China Lake is an important investment in our future. Senator King mentioned the connection the Muskie family personally had with China Lake owning a camp on its shore.
Pingree stated, “It was our fellow Mainer, Senator Ed Muskie, who wrote the clean water act half a century ago. Since then, it has been directly responsible for restoring and maintaining waters across the nation including right here in China Lake. Senator Muskie would be proud to see how much progress all of you at the China Lake Association have made to restore and protect the lake’s water to continue implementing the provisions of the Clean Water Act.”
The annual water quality report for China Lake was presented by Robbie Bickford, Water Quality Manager of Kennebec Water District (KWD). According to Bickford, “The results of the testing indicate China Lake is maintaining a steady state with a slight improvement in water quality over the past 10 years.” The full report can be found in the KWD newsletter which can be accessed here on ChinaLakeAssociation.org.
Bickford also provided updates on two projects Kennebec Water District accomplished this past year and are ongoing to protect water quality. KWD, with help from a grant from Project Canopy, reforested six acres on land KWD purchased in the early 1900s. Working with residents down in that area, KWD planted about 6,000 little seedlings with a mixture of black spruce, red spruce and red pine. In the fall of 2021, KWD developed a harvest plan in conjunction with a forest management plan. The goal is to achieve a mixed age, multi-species stand on all KWD land to maintain sustainable erosion control. KWD postponed last winter’s harvest until the winter of 2023 due to the warm conditions. Bickford explained that ideally the ground should be frozen during the harvest to prevent as much soil disruption as possible.

Bob O’Connor
The annual loon count was presented by Bob O’Connor, CLA board member. O’ Connor mentioned he has been counting loons on China Lake for 33 years, a third of a century. He was pleased to announce the count is up from 25 to 34. O’Connor announced another loon project in the works to help increase the loon population.
Karen McNeil, an undergraduate studying wildlife ecology and an intern for Maine Lakes, briefly presented information about the Loon Restoration Project. This project is intended to increase the loon productivity, while decreasing the mortality through establishing nesting rafts in ideal locations. Bill Powell, CLA board member is leading this initiative for the CLA and plans to launch an artificial nesting raft next year on China Lake. They are looking for more volunteers to build and monitor the raft for signs of nesting and chicks. Contact the CLA for more information about how to get involved.
Landis Hudson, executive director of Maine Rivers, made an upbeat presentation about the completion of the alewives restoration to China Lake and what this means to the regional ecology. This nearly ten-years-long project was headed up by the nonprofit organization Maine Rivers, in collaboration with the towns of China and Vassalboro, the Maine Department of Marine Resources, the Kennebec Water District, the Sebasticook Regional Land Trust, and the China Region Lakes Alliance. The China Lake Alewife Restoration Initiative hopes to reclaim the balance of wildlife in the water, air and land that existed prior to the dams construction centuries ago by restoring alewife passage. For the first time since 1783, alewives are making the trip from the ocean through the Kennebec River to China Lake to spawn. Nate Gray, a scientist with Maine Department of Marine Resources, manufactured a fish counter to get initial counts. The numbers of alewives making it through the fishways at the Box Mill Dam reached expectations.
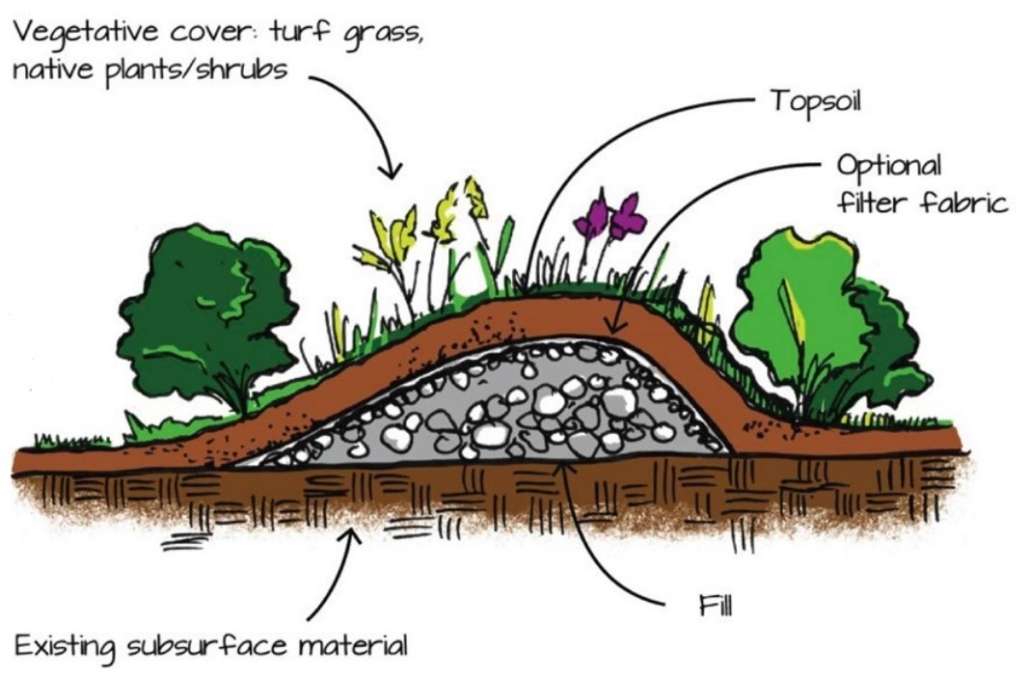
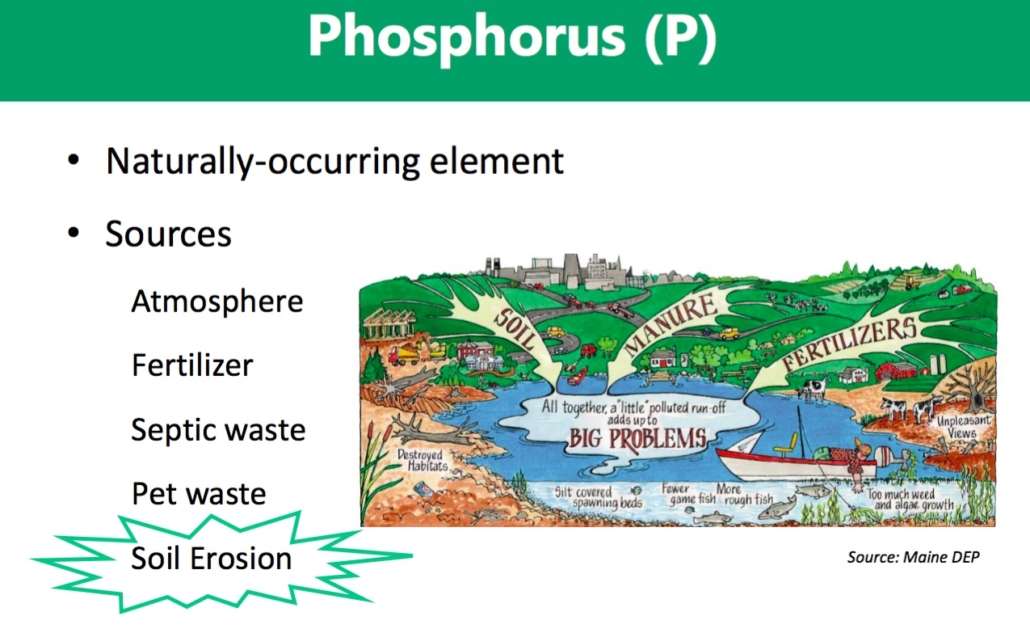
Eric Lind, vice president of CLA, spoke about the 2022-2031 China Lake Watershed-Based Management Plan (WBMP). The plan outlines management strategies and a 10-year schedule of steps to increase efforts to reduce the external phosphorus load by addressing existing nonpoint source (NPS) pollution throughout the watershed and limit new sources of phosphorus from future development and climate change. The plan significantly reduces the internal phosphorus load through inactivation of phosphorus in lake bottom sediments, and monitors and assesses improvements in China Lake’s water quality over time.
The 2022 launch of the WBMP is the culmination of a two-year comprehensive watershed survey, performed with help from CLA volunteers in partnership with Maine Department of Environmental Protection (DEP) and technical leaders. The survey identified sources of pollution, which included an assessment of gravel roads and developed properties in the watershed. The information from the survey was used in China Lake’s ten-year watershed management plan; the plan will help the CLA qualify for federal funding grants under the Clean Water Act. The China Lake Watershed-Based Management Plan is available on the CLA website.
Why is a watershed based management plan important? As reported August 5, 2022, in the Morning Sentinel and the Kennebec Journal, North Pond, in Smithfield, in the Belgrade area, is experiencing extreme algae blooms that have diminished the water clarity to only four feet. People are advised by the state Department of Environmental Protect to limit lengthy exposure to the pea soup green water and to have no exposure when water clarity reaches only three feet. There was no watershed management plan in place for North Pond. The North Pond Association has recently received a grant to establish a plan.
The last speaker of the CLA annual meeting was Judy Stone, Colby College professor and LakeSmart Award property owner, discussing forests, buffers and water quality. Stone provided property owners with sound advice on maintaining a canopy of diverse trees and permeable ground foliage to capture and filter stormwater.
The meeting closed with a strong vote of confidence for the re-election of the current leadership team: President Stephen Greene, Vice President Eric Lind, Secretary David Preston. An opening exists for a treasurer to replace retired treasurer Elaine Philbrook. The board of directors includes Robbie Bickford, Wayne Clark, Bruce Fitzgerald, Marie Michaud, Bob O’Connor, and Bill Powell, all of whom serve with the officers as volunteers managing the business and conducting the affairs of CLA.
The China Lake Association stands for “Preserving China Lake for Future Generations Through Environmental Stewardship and Community Action.” CLA officers and directors hold monthly meetings to drive growth and development of the organization. Stephen Greene invites interested people to attend. Contact him at stephencraiggreene@gmail.com to attend board meetings, become more involved, or discuss your thoughts about CLA.



 To the editor:
To the editor: