Up and down the Kennebec Valley: Agriculture & Inventions – Part 2
by Mary Grow
Colby College historian Earl H. Smith found four more local inventors besides Hanson Barrows and Alvin Lombard, whose work was last week’s topic. They were William Kendall, of Fairfield, and Waterville; Laroy Starrett, of China and Newburyport, Massachusetts; and in the 20th century, Martin Keyes and Frank Bunker Gilbreth.
An on-line genealogy says Captain William J. Kendall, Jr., was born Jan. 2, 1784, in Kendall’s Mills. Kendall’s Mills, named after William, Jr.’s, father, was until 1872 the name for the part of Fairfield that is now the business district.
The Fairfield bicentennial history says the senior William Kendall was a Revolutionary War veteran. He is referred to as “General” Kendall, and Smith called him a “Revolutionary War general”; your writer found military records consistently say he was a private during the Revolution.
In 1780, he bought most of the area that is now downtown Fairfield and “took over” a saw and grist mill started two years earlier by Jonas Dutton. With it he acquired the first Fairfield dam that Dutton built between the west shore of the river and the westernmost island (now Mill Island).
The senior William Kendall married Abigail Chase on Christmas Day 1782. The Fairfield historians wrote that she lived upriver at Noble’s Ferry (near the present Goodwill School); Kendall paddled his birch-bark canoe to the ferry, where they got married, and let the current bring them back to Kendall’s Mills.
William, Jr., was born Jan. 2, 1784, probably in William Sr., and Abigail’s first house, “a log house near the river” close to the present intersection of Main Street and Western Avenue. An on-line genealogy lists the younger Kendall’s occupations as “millwright & mill owner, inventor.”
His first mill, according to the multi-authored chapter on businessmen in Edwin Carey Whittemore’s history of Waterville, was on Ticonic dam, south of the Waterville-Winslow bridge. No date is given.
A list of early patents found on line says Kendall’s patent for a “reciprocating sawmill” was issued Dec. 31, 1827. He was then from Waterville.
 Smith agreed with the location, but not with the date. He wrote that there is disagreement over the first inventor of the circular saw, but probably the first one in Maine was “around 1845 in Waterville,” and was Kendall’s work.
Smith agreed with the location, but not with the date. He wrote that there is disagreement over the first inventor of the circular saw, but probably the first one in Maine was “around 1845 in Waterville,” and was Kendall’s work.
Whittemore’s history accepts the 1827 date. Actually, 1827 might be late: another on-line source dates the patent to 1826, and Whittemore quotes a Jan. 4, 1827, Waterville newspaper article describing the Jan. 1 presentation of a gold medal to Kendall “in approbation of the improvement he has made in the circular saw.”
The newspaper report said Mayor Bolcom made the medal, which looked like a circular saw. (This statement makes sense only if “Mayor” is a first name rather than a title, as Waterville did not become a city until January 1888.)
The Waterville history says Kendall’s saw “was six feet in diameter, built of boiler plates riveted together; and the steel teeth, about three by four inches, were fastened in proportion by fifteen or twenty rivets for each tooth.”
Smith and the Fairfield historians agree on the importance of this invention. Smith said the circular saw “doubled the speed” of making logs into boards, with one circular saw doing the work of four up-and-down saws. Whittemore added that the saw turned a single pine log into “3310 feet of clear boards.”
Whittemore told the story of workers from a traveling “caravan” that charged 25 cents admission: the workers came to Kendall’s mill and contributed 25 cents each for a visit, “saying that it was more of a show to see the saw walk through a log than it was to see their own exhibition.”
The Fairfield historians wrote that the invention of the “circular log saw blade” “revolutionized the industry.” They added, “It is a sad commentary to note that General William Kendall did not live to see the success of his son’s invention, as he died that same year [Aug. 11, 1827, according to on-line sources].”
The Fairfield history says two generations of Kendalls ran the mills into the 1830s, when the family sold them.
In later years, Whittemore said, Kendall made “an invention pertaining to the casing of water wheels, which he patented” and installed in Fairfield and Waterville mills.
The on-line genealogy says Kendall married Sarah Chase, who was born Nov. 22, 1787, in Andover, New Hampshire, and died in Gardiner in January 1822, when she was only 34. The couple had seven children. Whittemore located the Kendall home “near the west end of Ticonic bridge.”
Kendall died Nov. 27, 1872, in Fairfield, according to the genealogy.
* * * * * *
With China-born inventor Leroy S. Starrett, the factual disagreements start with his name. Smith called him Leroy S. Starrett; a reproduction of patent number 47,875, issued May 23, 1875, calls the inventor “Le Roy S. Starrett.”
The China bicentennial history and on-line sources say Laroy S. Starrett. The Davistown Museum website lists him as “Laroy (often incorrectly recorded ‘Leroy’) S. Starrett.” (The Davistown Museum website says the museum in Liberty and Hulls Cove, Maine, that specialized in hand tools has closed.)
Find a Grave says his full name was Laroy Sunderland Starrett.
There is general agreement that Starrett was born April 25, 1836, in China, Maine. Find a Grave lists his parents as Daniel Dane Starrett (born Nov 25, 1802, in Francestown, New Hampshire; died Feb. 9, 1896, in South China), and Anna Crummett Starrett (born Jan. 27, 1803, in Boothbay; died March 3, 1875, in South China).
There is further agreement that one of Laroy Starrett’s job descriptions is “inventor.” Others include farmer, businessman, carpenter and tool manufacturer.
The China bicentennial history says when he was 17, Starrett began working for nearby farmers to earn money to help pay off the mortgage on the family farm. In 1855 or soon thereafter, he moved to Newburyport, Massachusetts, where he either worked for a local widow on her farm or rented a farm (sources again differ).
Though he was a successful farmer, winning prizes at the local fair, he soon turned his attention to inventing metal gadgets.
The Find a Grave website has a 28-item list of his patents. Some are specific, like his first and best-known, the meat chopper or meat cutter for which he received a patent on May 23, 1865. It is followed by “shoe studs and hooks,” Jan. 28, 1868, and a “combination square”, with the patent dated Feb. 26, 1879.
The Newburyport, Massachusetts, history website adds “a washing machine and a butter worker.” In all, Starrett received 100 patents, many for precision tools, a lot of which are still used today.
The “combination square” is probably the invention Smith credited to Starrett, describing it as a “combination square and ruler with a sliding head.” Smith added, “The tool, essentially unchanged, is still routinely found in toolboxes of woodworkers everywhere.”
The Newburyport website writer believed Starrett’s invention of the meat cutter in 1865 led the family to move from rural to downtown Newburyport. Citing city directories, the website says Starrett made and sold meat cutters from an address on Merrimac Street (shown on contemporary maps as paralleling the Merrimack River).
In 1867 and 1868, Starrett “was advertising the meat cutter/chopper a lot in the local newspapers,” the website says.
The story continues, “He was so successful that he left Newburyport to manufacture his inventions…in Athol, Massachusetts, which is in the upper western part of the state near Gardner.”
There, Wikipedia says, Starrett founded L. S. Starrett in 1880, so he could manufacture the combination square he had patented two years earlier “and other precision tools.” The company has steadily grown and expanded into an international business; websites list Douglas Arthur Starrett as the current CEO and president.
Douglas Arthur Starrett lives in Athol, Massachusetts; he is 72 years old, according to the most up-to-date site your writer found. Patient genealogical research suggests that he is the great-great-great-grandson of Laroy Sunderland Starrett.
Laroy Starrett and Newburyport resident Lydia Webb Bartlett (Sept. 4, 1839 – Feb. 3, 1878) were married in 1861. They had five children, a son born in 1862 and a second, born in 1869, who lived only 13 months, according to Find a Grave.
The youngest daughter was born Jan. 10, 1878, in Athol. Lydia’s death less than a month later left Starrett with a 15-year-old son and three daughters, one an infant.
The China history says Starrett was deaf from about 1904 on. Widowerhood and deafness did not end his career, or “his generous concern for others,” the history says. He supported charitable projects in Athol, and in South China gave the Chadwick Hill cemetery a $1,000 gift in 1916, another $600 in 1917 for perpetual care of the Starrett family lots “and an even larger sum in 1920.”
Starrett died April 23, 1922, in Saint Petersburg, Florida. He and Lydia are among several generations of the Starrett family buried in Athol’s Silver Lake cemetery.
* * * * * *
Next week: a bit of information about Martin Keyes and Frank Gilbreth.
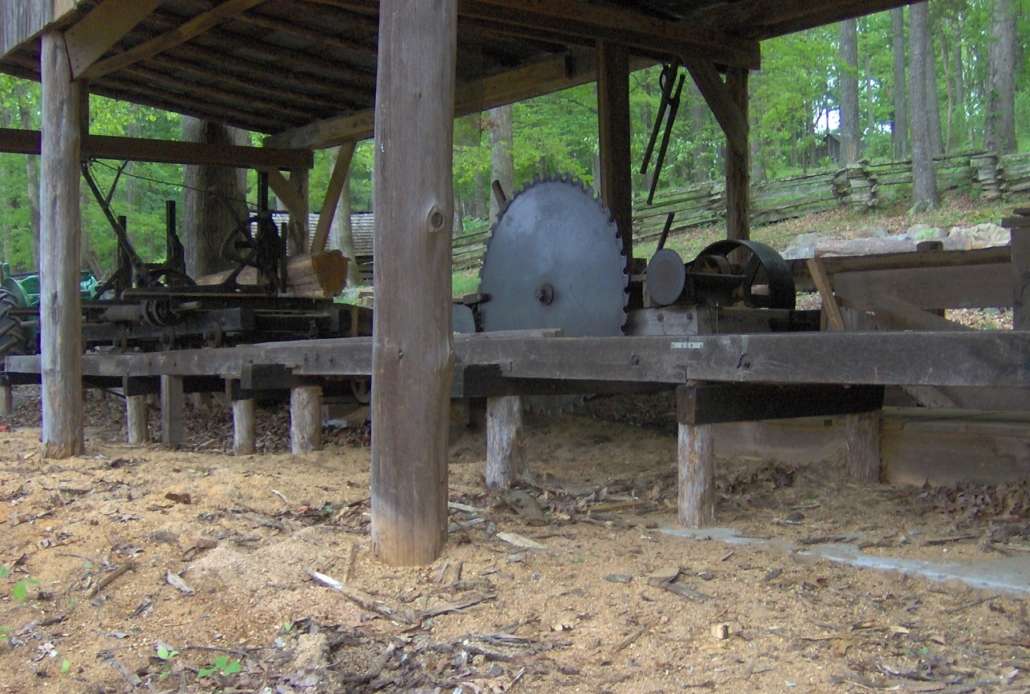
Up and Down sawmills
The Fairfield historians explained that sawmills in the 1700s and early 1800s used an up and down saw. Milton Dowe, in his 1954 history of Palermo, gave a more complete description of such a saw.
He wrote that water coming over a dam powered a water wheel. Attached to the water wheel was a crankshaft connected to an “arm” connected to the saw frame.
The saw frame was rectangular, “about six feet long and eight feet wide…with the saw fastened in the center.” The saw itself was similar to an ice-cutting saw and was “about six feet long and seven inches wide.”
Dowe continued, “The frame holding the saw was set in guides in an upright position in such a way that the short arm from the crankshaft, as the waterwheel turned, would push and pull the frame up and down.”
A carriage held a log that was pushed forward “by a rachet on a feed wheel” each time the saw blade came down. Each log was sawed into boards about an inch at a time, Dowe wrote.
Main sources
Fairfield Historical Society Fairfield, Maine 1788-1988 (1988).
Grow, Mary M,. China Maine Bicentennial History including 1984 revisions (1984).
Smith, Earl H., Downeast Genius: From Earmuffs to Motor Cars Maine Inventors Who Changed the World (2021).
Whittemore, Rev. Edwin Carey, Centennial History of Waterville 1802-1902 (1902).
Websites, miscellaneous.
Responsible journalism is hard work!
It is also expensive!
If you enjoy reading The Town Line and the good news we bring you each week, would you consider a donation to help us continue the work we’re doing?
The Town Line is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit private foundation, and all donations are tax deductible under the Internal Revenue Service code.
To help, please visit our online donation page or mail a check payable to The Town Line, PO Box 89, South China, ME 04358. Your contribution is appreciated!





Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!