SCORES & OUTDOORS: Turkey vultures becoming more and more common in central Maine
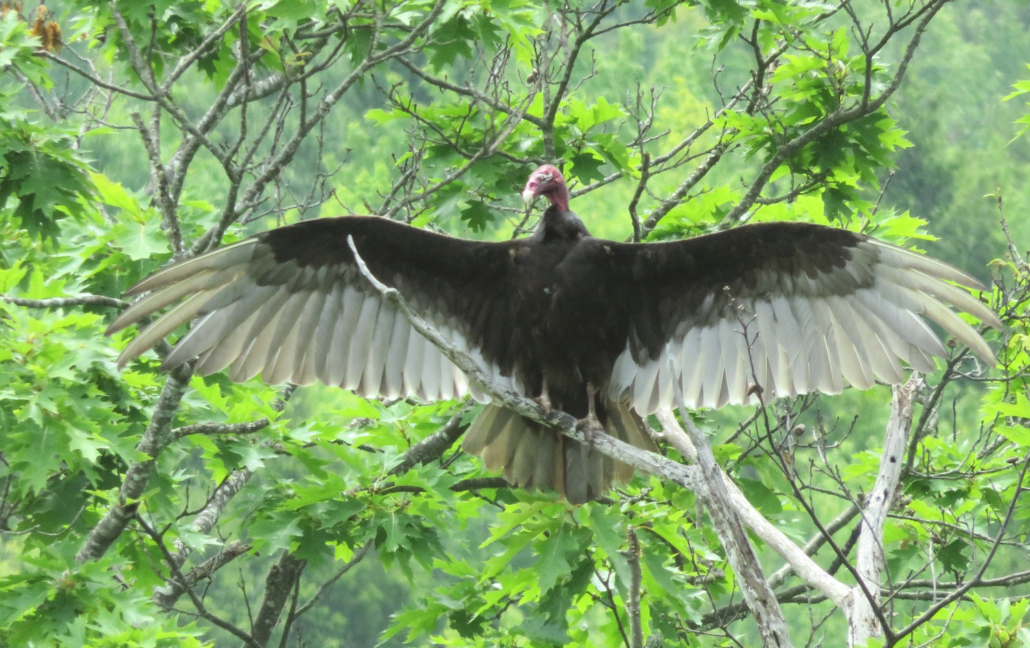

SOAKING THE SUN: This turkey vulture was photographed by Pat Clark, of Palermo, stretching its wings while soaking in the sunshine.
 by Roland D. Hallee
by Roland D. Hallee
I remember as a young boy growing up of going to the “movies” at the old State Theater, on Silver St., in Waterville (now Cancun Restaurant). It was the Saturday kids’ marathon. You would get to the theater at 10 a.m., and probably wouldn’t come out until dark. There were cartoons galore, news reels, several feature films, and even a commercial for popcorn in the lobby. (For 25-cents, you got admission to the theater, a bag of popcorn and soda – and get change back.)
One of the things I remember well, and are still my favorites today, were the old film noir westerns. The films were marked with poor lighting, corny sound effects and acting – but Gene and Roy could sing you a tune, and beat up the bad dudes. Pretty versatile guys to have around.
One scene would always be of a vulture circling overhead, signaling the presence of a corpse, or a carcass of a dead animal near a watering hole, an indication of a poisoned pool.
I had never seen a real vulture. I thought they only existed where the cowboys roamed the western range.
Later in life, around the 1980s, I saw my first real vulture on top of French’s Mountain, in the town of Rome. However, recently I have seen a growing population of the turkey vultures in central Maine. First, on the Nelson Rd., in Vassalboro, and recently on Chase Ave., in Waterville, near the Delta Ambulance headquarters. Last Sunday, I saw four of them in the road.
Its range is from southern Canada to the southermost tip of South America.
The turkey vulture, Cathartes aura, or turkey buzzard as it is known in some North American regions, is a scavanger that feeds almost exclusively on carrion. It finds its food using its keen eyes and sense of smell, flying low enough to detect the gasses produced by the beginnings of the process of decay in dead animals. This is an uncommon ability in the avian world. The olfactory lobe of its brain, responsible for processing smells, is particularly large compared to that of other animals. Lacking a syrinx, the vocal organ of birds, its only vocalizations are grunts or low hisses. It nests in caves, hollow trees, or thickets. It has very few natural predators. In the United States, the vulture receives legal protection under the Migratory Bird Treaty Act of 1918.
It is listed as a species of Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) red list. Populations appear to be stable, thus has not reached the threshold of inclusion as a threatened species, which requires a decline of more than 30 percent in 10 years or three generations.
In the U.S. it is illegal to take, kill, or possess turkey vultures, their eggs, and any body parts including but not limited to their feathers; violation of the law is punishable by a fine of up to $100,000 for individuals or $200,000 for organizations, and/or a prison term of one year.
Turkey vultures appear black from a distance but up close are dark brown with a featherless red head and pale bill. While most of their body and forewing are dark, the undersides of the flight feathers (along the trailing edge and wingtips) are paler, giving a two-toned appearance.
The turkey vulture received its common name from the resemblance of the adult head of a wild turkey, while the name vulture is derived from the Latin word vulturus, meaning “tearer,” and is a reference to its feeding habits.
The wingspan of a turkey vulture is between 63 – 72 inches, has a length of 24 – 32 inches and weighs 1.8 to 5.3 pounds. Northern vulture are generally larger than the ones from its southern range. It is the most abundant vulture in the Americas. The global population of the turkey vulture is estimated to be 4.5 million individuals.
The turkey vulture is gregarious and roosts in large community groups, breaking away to forage independently during the day. It roosts on dead, leafless trees, and will also roost on man-made structures such as water and microwave towers. Though it nests in caves, it does not enter them except during the breeding season. The turkey vulture lowers its night time body temperature to about 93 degrees F, becoming slightly hypothermic.
Turkey vultures are perceived as a threat by farmers due to the similar black vulture’s tendency to attack and kill newborn cattle. Turkey vultures will not kill live animals, but will mix with other flocks of black vultures and will scavenge what they leave behind.
The breeding season varies according to region. In the north, it commences around May and continues into August. They do not lay eggs in a nest, but rather on a bare surface. Females generally lay two eggs, but sometimes one and rarely three. The incubation period lasts between 30 – 40 days. Chicks are helpless at birth. The young fledge at about nine to ten weeks, and family groups will remain together until fall.
Turkey vultures are majestic but unsteady soarers. Their teetering flight with very few wingbeats is characteristic. Look for them gliding relatively low to the ground, sniffing for carrion, or else riding thermals up to higher vantage points. They may soar in small groups and roost in larger numbers. You may also see them on the ground in small groups, huddled around roadkill or dumpsters.
Turkey vultures are common around open areas such as roadsides, suburbs, farm fields, countryside, and food sources such as landfills, trash heaps, and construction sites. On sunny days, look for them aloft as early as 9 a.m.; in colder weather and at night they roost on poles, towers, dead trees, and fence posts.
Thankfully though, they are pretty harmless. Turkey vultures really do only eat dead flesh, so your pets and children are technically safe. When they gather together in trees though, people will often bring their children inside. They also can give people an eerie feeling when they circle overhead.
They have no incentive to attack humans and they lack the physical attributes that could pose a threat. Some vultures will spew projectile vomit as a defense mechanism, which is about the extent of their hostile behavior.
Again, like many other species I have observed, more and more of these critters are beginning to show up in the urban surroundings, where in the past they were only seen in rural areas.
Roland’s trivia question of the week:
Who is the only NFL quarterback in the Hall of Fame who is left handed?