TECH TALK: Are you human or robot? The surprising history of CAPTCHAs
 ERIC’S TECH TALK
ERIC’S TECH TALK
by Eric W. Austin
We’re all familiar with it. Try to log into your favorite website, and you’re likely to be presented with a question: Are you human or a robot? Then you might be asked to translate a bit of garbled text or pick from a set of presented images. What’s this all about?
There’s an arms race going on between website owners and internet spam bots. Spam bots want to log into your site like a regular human, and then leave advertising spam comments on all your pages. Website admins naturally want to stop this from happening, as we have enough ordinary humans leaving pointless comments already.
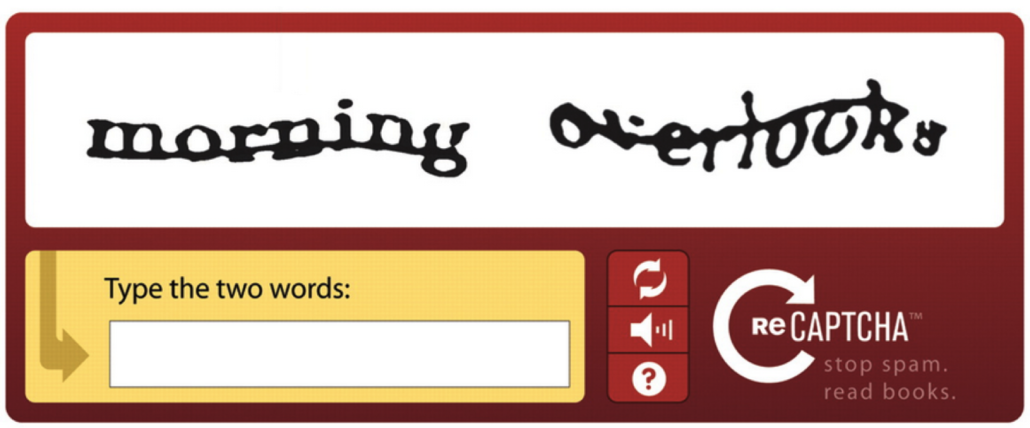
Although several teams have claimed ownership of inventing the technique, the term ‘CAPTCHA’ was first coined by a group of engineers at Carnegie Mellon University in 2001. They were looking for a way to allow websites to distinguish between live humans and the growing multitude of spam bots pretending to be human. They came up with the idea of showing a user distorted images of garbled words that could be understood by a real person but would confound a computer. It was from this idea that the ubiquitous CAPTCHA emerged.
CAPTCHA is an acronym that stands for ‘Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart.’
Around this same time, The New York Times was in the process of digitizing their back issues. They were employing a fairly new computer technology called Optical Character Recognition (OCR), which is the process of scanning a page of type and turning it into searchable text. Prior to this technology, a scanned page of text was simply an image and not searchable or capable of being cataloged based on its content.
Old newsprint can be difficult to read for computers, especially since the back catalog of The New York Times stretches back more than 100 years. If the ink has smeared, faded or is otherwise obscured, a computer could fail to correctly interpret the text.
The New York Times got the brilliant idea of using these difficult words as CAPTCHA images, utilizing the power of internet users to read words a computer had failed to recognize. The project was reinvented as ‘reCAPTCHA.’
In 2009, Google bought the company responsible for reCAPTCHA and began using it to help digitize old books for their Google Books project. Whenever their computers run into trouble interpreting a bit of text, a scan of those words is uploaded to the reCAPTCHA servers and millions of internet users share in the work of decoding old books for Google’s online database.
I bet you didn’t realize you’re working for Google every time you solve one of those garbled word puzzles!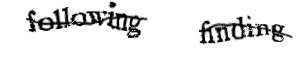
Of course, artificial intelligence and OCR technology has improved a lot in the years since. Now you are more likely to be asked to choose those images that feature street signs, rather than to solve a bit of distorted text. In this way, Google is using internet users to improve its artificial intelligence image recognition.
Soon computers will be smart enough to solve these picture challenges as well. In fact, the latest version of CAPTCHA barely requires any input from the internet user at all. If you have come to a webpage and been asked to check a box verifying that, “I’m not a robot,” and wondered how this can possibly filter out spam bots, you’re not alone. There’s actually a lot more going on behind that simple checkbox.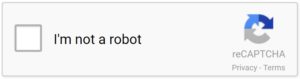
Invented by Google, and called “No CAPTCHA reCAPTCHA,” the new system employs an invisible algorithm behind the scenes that executes when you check the box. This algorithm analyzes your recent online behavior in order to determine if you are acting like a human or a bot. If it determines you might be a bot, you’ll get the familiar pop-up, asking you to choose from a series of images in order to verify your humanity.
This internet arms race is a competition between artificial intelligence’s efforts to pass as human and a website admin’s attempt to identify them. The CAPTCHA will continue to evolve as the artificial intelligence of spam bots increases to keep pace.
It’s an arms race we’re bound to lose in the end. But until then, the next time you’re forced to solve a garbled word puzzle, perhaps it will help ease the tedium to remember you’re helping preserve the world’s literary past every time you do!



 SCORES & OUTDOORS
SCORES & OUTDOORS Crows are common and widespread. Males tend to be larger than females. There are many species of crows but the one we most associate with is the American crow. They are large, distinctive birds with iridescent black feathers. Mature birds are usually 16 – 20 inches in length, with about 40 percent of which is tail. Their wingspan is approximately 33 – 39 inches. The life span of the American crow in the wild is 7 – 8 years, while they have been known to live up to 30 years in captivity.
Crows are common and widespread. Males tend to be larger than females. There are many species of crows but the one we most associate with is the American crow. They are large, distinctive birds with iridescent black feathers. Mature birds are usually 16 – 20 inches in length, with about 40 percent of which is tail. Their wingspan is approximately 33 – 39 inches. The life span of the American crow in the wild is 7 – 8 years, while they have been known to live up to 30 years in captivity. REVIEW POTPOURRI
REVIEW POTPOURRI

 For Your Health
For Your Health by Marilyn Rogers-Bull & Percy
by Marilyn Rogers-Bull & Percy GARDEN WORKS
GARDEN WORKS

