SCORES & OUTDOORS: Red foxes are abundant and widespread in all 16 Maine counties
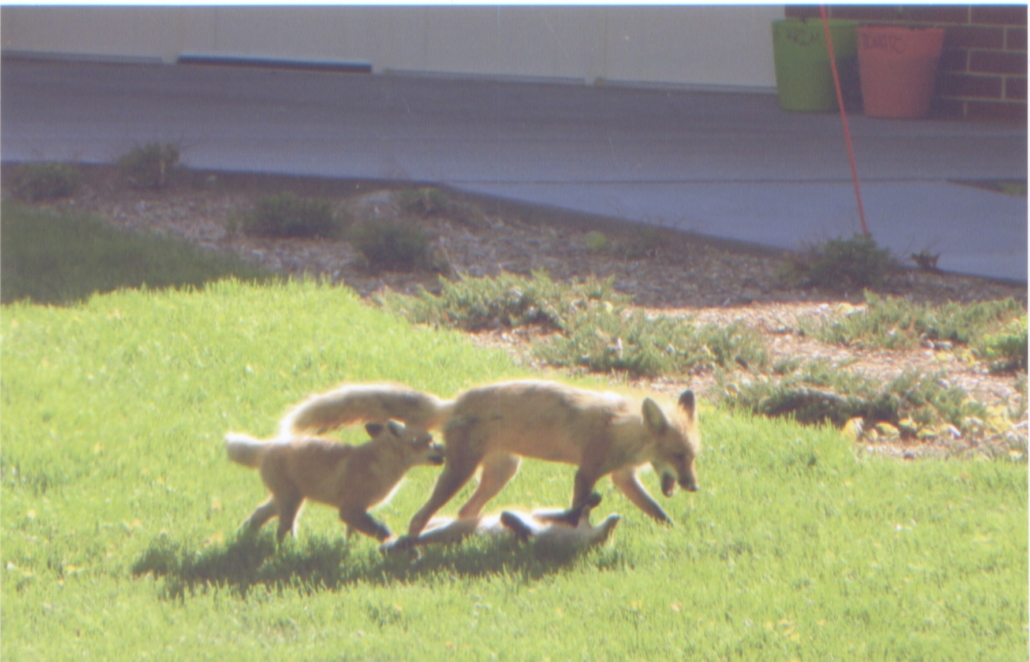

A mother red fox with her kittens rambling through the grounds at the Togus VA. (photo by Gary Kennedy)
 by Roland D. Hallee
by Roland D. Hallee
Over the last several weeks, I have been approached and told of numerous fox sightings. It seems they are becoming more abundant in our area. I have seen a few, on the roadways, from time to time, as they cross from one side to the other. They have also been spotted at camp, moving about from lot to lot.
Then, there is the sighting, by one of our supporters, of the somewhat rare gray fox.
Maine is fortunate to have two species of fox, the red fox, Vulpes vulpes, and gray fox Urocyon cinereoargenteus. Both species are similar in size, but there are some important differences in their appearance, behavior, and distribution.
The red fox is abundant and widespread, occurring in all 16 counties in Maine. Adult red foxes weigh 7-15 pounds and have a distinct red/orange appearance, white chest, black legs, and bushy white-tipped tail. Silver or cross foxes are an abnormal development of dark pigmentation in the fur of the red fox; they appear black, silver or a combination of red/black/grey and are less common than the typical red ones. Red foxes have keen eyesight and hearing, and are very agile, jumping up to six feet high. Red foxes have a special method of hunting with impressive pounces on prey hidden under the snow or ground.
The gray fox is abundant in southern and mid-coast Maine, and continues to expand into western and central parts of Maine. Gray foxes weigh about 10 pounds and are distinguished by their grizzled coloration, a hint of red on the neck, ears, and lower legs, and a black stripe down their tail. Gray fox are the only member in the canid (dog) family in North America that can climb trees. Red foxes can climb, but not as well as gray foxes.
Foxes are omnivores and eat a wide variety of plants and animals, depending on the season. Small birds and mammals are consumed, including mice, voles, rats, rabbits, and bird eggs. Foxes also eat insects, snakes, carrion, berries, apples, corn, seeds, and nuts.
Foxes are primarily nocturnal, including hunting during dawn and dusk, but foxes are occasionally seen out during the day, particularly during the spring/summer, as is the case right now, when rearing pups.
Foxes are found in diverse habitats and are quite tolerant of living near people. Foxes are common in agricultural landscapes and tend to do well with a mix of forest and fields.
Coyotes are predators of foxes but tend to be more wary of people, so foxes avoid coyotes by living near people.
Research suggests that humans create the conditions for conflict by deliberately or inadvertently providing animals with food and shelter. The Maine Department of Inland Fisheries and Wildlife urges you to use the following management strategies around your property to prevent or resolve conflicts and encourage your neighbors to do the same.
Seeing a fox out during the day is not a problem and does not mean the fox is sick! Never approach or handle wildlife. Enjoy watching the fox go about its business from a safe distance. Remember that fur coats are much thinner and patchier in the summer, especially for mother foxes who have put most of their energy into raising young.
Never feed wildlife. Once an animal is fed, it will return, lose its fear of people, and could become aggressive.
If you have had conflicts in the past and have a bird feeder, consider planting native plants instead. Bird feeding can create a chain of events that are not always obvious. Dropped seed attracts many wildlife species who feed on the seeds or predators who feed on the rodents that increase as a result of a bird feeder.
Store your trash inside buildings, use garbage cans with locking lids, and bring your garbage cans to the curb the morning of pick up.
Securely cover and fence compost piles or use a compost bin. Never throw dairy or animal matter into compost, since it can become smelly and attract animals. Regularly mixing in some dirt or leaves to your pile will also reduce the scent and allow the foods to break down more quickly into compost.
Foxes and other predators will kill free-ranging chickens and other small livestock that are not secured in a shelter. Protect your livestock from predation by using a predator-proof pen with well-fitted doors and locks and electric fencing.
Small livestock should be confined to their pens during vulnerable periods from dusk until dawn.
Foxes can carry diseases, but people can protect themselves by keeping a safe distance from wildlife and vaccinating their pets. Common fox diseases include mange, rabies, and canine distemper.
Foxes are very tolerant of people and will den in a variety of places, including near roads, in yards, or under buildings. In most cases, the fox family will move if there is a lot of disturbance. Be a responsible pet owner and never let your dog harass wildlife. If you want to encourage the foxes to move, simply pour some bleach or ammonia at the entrance of the den, leave a portable light on, or a radio on overnight. This will encourage them to move to an alternative den.
Prevent wildlife from denning under your porch, deck, or buildings by closing off holes during the fall. Close off these areas with quarter-inch hardware cloth, boards, metal flashing or other sturdy barriers.
In the rare case that there is an aggressive-acting animal, call the nearest dispatch center for help:
Augusta 1-800-452-4664; Bangor 1-800-432-7381; Houlton 1-800-924-2261.
Roland’s trivia question of the week:
Which Red Sox first baseman went 238 games without committing an error between 2006 and 2008?