SCORES & OUTDOORS – Be cautious of the wild parsnip
 by Roland D. Hallee
by Roland D. Hallee
A reader wrote last week how she had been trying for a couple of years to identify a tall yellow-flowered roadside weed until someone told her it was wild parsnip. Unable to find much information about it, she turned to this column.
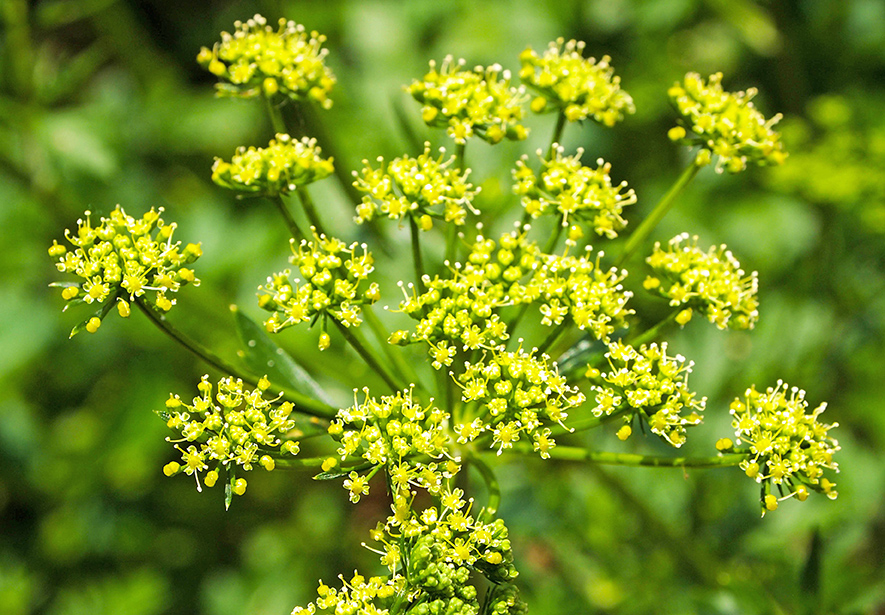
Wild parsnip, Pastinaca sativa, is among the rapidly increasing weeds in many areas. As wild parsnip has spread, so has the realization that human exposure often leads to serious burns and blisters on the arms and legs. Being able to readily identify wild parsnip and early detection of infested areas will minimize inadvertent and excessive exposure to this plant and the often painful results that follow.
The species is native to Eurasia, and may have been introduced as a vegetable as plants have long, thick, white to yellowish taproots that are edible. True parsnip plants have larger roots than wild parsnip. The entire plant has a parsnip odor. Cattle will not eat wild parsnip but deer may feed on it, and birds and small mammals eat the seeds.
The plants are most abundant in sites dominated by perennial grasses that are mowed once or twice a year.
Why the explosion of wild parsnip? Only Mother Nature knows for sure. Birds and mammals eat the seeds and they may be spreading the problem from site to site. There is no doubt that the delay in mowing roadsides until mid summer as an official roadside management policy of the state and towns opens the door for this plant to complete its life cycle, and produce ripe seeds well before any mowing is done. Wild parsnip is tolerant of a wide range of conditions, including dry and wet areas. It is shade tolerant, but prefers sunny conditions. Depending on the habitat and growing conditions, individual flowering plants range to over four feet in height.
Also, when roadsides and pastures are mowed in July and August, parsnip seeds probably move as hitchhikers on the mowers. Mowing also creates a much more favorable environment for parsnip seeds to germinate than if the sites were left undisturbed. Relatively mild winters may enhance survival of wild parsnip plants that germinate and become established in the fall.
Wild parsnip has a long germination period, but the optimum time for germination is in the early spring, and that is when most germination occurs. Most fall germinated seedlings die during winter. Wild parsnip seedlings are among the first plants to “greenup” early in the spring.
Rosettes grow close to the ground and bear leaves averaging six inches in height. Flowering plants produce a single, thick stem that contains hundreds of yellow umbellate flowers. The lateral flowers often overtop the terminal flowers.
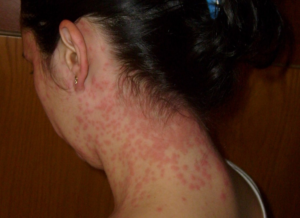
But, the most important thing for humans to remember is to avoid contact with the plant. Humans develop a severe skin irritation from contact with its leaves. Plants have chemicals called psoralens that cause an interaction between plant and light that induce skin inflammation.
Experts are warning people to stay away from wild parsnip after a Vermont woman was severely burned after being exposed to the sap.
The plant grows along rural roads and in meadows throughout the state. Wild parsnip is not native to Maine and has a deep vertical ridge on its stalk. The flowers come in clusters of tiny yellow flowers similar to Queen Anne’s Lace.
A woman in Vermont fell into a wild parsnip plant and suffered horrific burns after her legs were exposed to the sap and she spent time in the sun.
“It is soluble,” said Maine State Horticulturist Gary Fish. “It goes into the skin and that’s when you are going to have damage to the skin which turns into blisters when you have sun exposure.”
People walking through vegetation should wear long sleeves and pants and stay away from plants that look like wild parsnips.
Wild parsnip has sap that has psoralens in it — naturally occurring organic compounds that can kill skin cells that protect people from ultraviolet radiation. When the sap touches the body, it can cause blisters and symptoms resembling symptoms from a burn.
Once the sap is absorbed by the skin, they are energized by UV light on both sunny and cloudy days. They then bind to DNA and cell membranes, destroying cells and skin. Parsnip burns usually occur in streaks and elongated spots, reflecting where a damaged leaf or stem moved across the skin before exposure to sunlight.
Wild parsnip burns differ from the rash caused by poison ivy in several aspects. First, everyone is sensitive to wild parsnip and you do not need to be sensitized by a prior exposure to develop burns or blisters. You can brush against wild parsnip plants and not be affected. Parsnip is dangerous only when the plant sap from broken leaves or stems gets on your skin. Lastly, the parsnip “burn” is usually less irritating than poison ivy’s “itch.”
After about 3 days, the symptoms start to get better. Eventually, like after a bad sunburn, the burned skin cells die and flake off. As symptoms improve, the rash may appear lighter or darker. Discoloration and sensitivity to sunlight in the affected areas can remain for up to two years.
Wild parsnip grows abundantly on our roadsides. Some people mistake it as ragweed, and rightfully so. There is, however, many dissimilarities once you see them side by side.
If you develop a rash or blisters, go to the hospital or a clinic for treatment.
There are other plants in the family that can be harmful as well: Cow Parsnip, a native plant, with white flowers; Giant Hogweed, an invasive species, with white flowers similar to cow parsnip.
When it comes to wild parsnip, unless you are absolutely sure it is something else, don’t touch it.
Roland’s trivia question of the week:
In 1975, the Red Sox played the Cincinnati Reds in what is called the “Greatest World Series ever.” Who hit an eighth inning three-run homer in game 6 to tie the score, and set up Carlton Fisk’s 12th inning iconic home run?









 An owl is a wise bird: Fiction – Some people think owls look wise because of their eyes. But for a bird its size, the owl has a tiny brain. An owl never moves its eyes to look for prey, but, instead, moves its whole head from side to side.
An owl is a wise bird: Fiction – Some people think owls look wise because of their eyes. But for a bird its size, the owl has a tiny brain. An owl never moves its eyes to look for prey, but, instead, moves its whole head from side to side. Rats desert a sinking ship: Fact – Rats will jump overboard if a ship is sinking. But that is true of any animal that can swim. Rats sometimes desert a ship even if it isn’t sinking. In the days of sailing ships, it was a common sight to see packs of rats jumping overboard. The ships were slow and would be at sea for months. By the time they returned to port, there was little food left for the rats so when the ship came close to shore, they would dive overboard and swim to land in search of food.
Rats desert a sinking ship: Fact – Rats will jump overboard if a ship is sinking. But that is true of any animal that can swim. Rats sometimes desert a ship even if it isn’t sinking. In the days of sailing ships, it was a common sight to see packs of rats jumping overboard. The ships were slow and would be at sea for months. By the time they returned to port, there was little food left for the rats so when the ship came close to shore, they would dive overboard and swim to land in search of food.