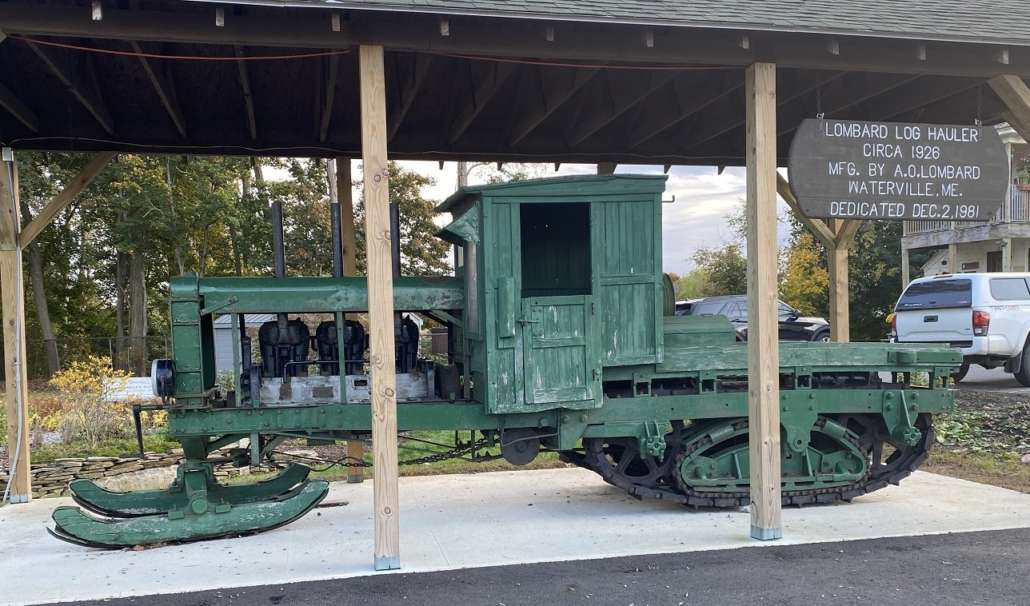
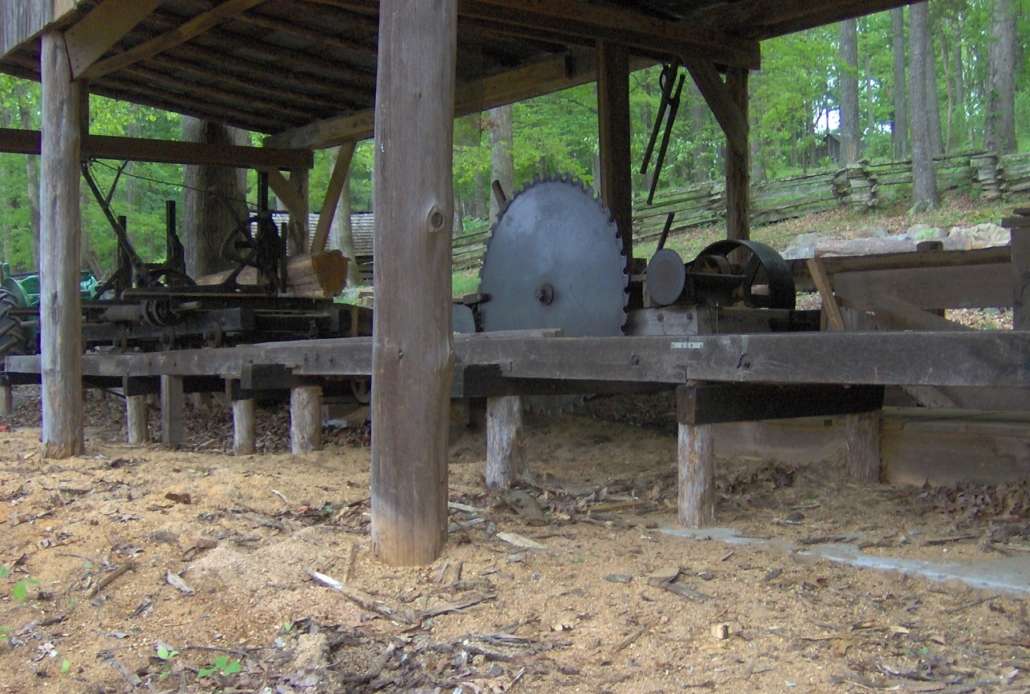
The Lombard log hauler, one of only six remaining, at its home at the Redington Museum, in Waterville. (photo by Roland Hallee)
Previous articles have talked about how agricultural work changed from the 1700s through the 1800s, as manpower was replaced by animal-power and then machines.
Other changes, too, helped farmers produce more or expend less effort or both. One example is the development of wire for fences. (Barbed-wire fencing was mentioned in the Sept. 7 issue of The Town Line, in the account of the skaters who burned part of a farmer’s stump fence for bonfires and redeemed themselves by putting up barbed wire as a replacement).
In his history of Windsor, Linwood Lowden wrote, “As early as the year 1861, it had been modestly estimated that an old-fashioned wood or stone fence takes a strip of land at least four feet wide out of cultivation.”
Losing a four-foot strip was not a problem while a farmer was battling to clear trees and rocks to make fields to grow food for his animals and his family. When he intended to sell some of what he raised, and when wood became scarce, he needed different fencing material.
Wire fences were the solution, Lowden wrote. Citing an 1882 Maine Board of Agriculture report, he said the first fence wire might have might have been made as early as 1815.
The industry was “still in its infancy” in the 1820s, with an individual worker “able to produce but from 15 to 40 pounds of fence wire per day.” By 1882, new technology made it possible for a single worker to “produce between 1,000 to 2,500 pounds per day.”
(There is an on-line controversy about who invented wire. The candidate list begins with Thomas Malham, Sheffield, England, in 1830; Jean Francois Martin, of France, about the same time; and other contemporary foundry owners, unnamed. Another historian calls their nominations “manifest nonsense.” He says Egyptians in the time of the pharaohs [3,000 B.C. and following centuries] made wire from gold, silver and copper, and wire made from iron “was achieved about 1450, in Augsburg [Germany].”)
Barbs came later. Wikipedia says Lucien B. Smith, of Kent, Ohio, got the first patent for barbed wire in 1867 and “is regarded as the inventor.” In 1874, Joseph F. Glidden, of DeKalb, Illinois, made enough “modifications” (or, another source says, “invented a practical machine for its manufacture”) to get his own patent.
The Board of Agriculture report said in 1874, the United States had 10 miles of three-strand wire fence (in 37 states). By 1882, there were 166,000 miles (in 38 states; Colorado was added in 1876).
* * * * * *
The invention of wire fencing, unlike the use of it, had nothing to do with any part of Maine. However, Maine had its share of inventors, including some from the central Kennebec Valley area.
Vassalboro historian Alma Pierce Robbins named two Vassalboro inventors who helped with farm and other outdoor work. One was the comparatively well-known Alvin Lombard (see below).
The other, more obscure, was Hanson G. Barrows, who, she wrote, invented a mowing machine & a snowplow; models extant in 1971 “go to prove what a true genius he was.”
(On-line sources on the origin of the mechanical reaper [which the web discusses in reply to requests for mowing machines] do not mention Barrows, focusing instead on the competition between Obed Hussey [1792-1860] and Cyrus McCormick [1808 or 1809 – 1883 or 1884] in the 1840s and 1850s. Colby College historian Earl H. Smith included both these inventors in his 2021 book, Downeast Genius: From Earmuffs to Motor Cars Maine Inventors Who Changed the World.)
Hussey was born in a Quaker family, in Hallowell; they moved to Nantucket, Massachusetts, when he was a child, and his work was done in Maryland and Ohio. Smith commented that Hussey realized Maine was an unfair place to test his reaper – not only was Maine farmland “hilly and difficult to plow, the real curse was the rocks, which often broke the shafts and blades of his machines.”
Smith connected Virginia-born McCormick with Maine only through his “War of the Reapers” with Hussey, which covered much of the United States; in 1851 was part of London’s Great Exhibition, “the first world’s fair”; and later moved to France and elsewhere in Europe.
Robbins wrote that Hanson Barrows (1831-1916) was the oldest of three sons and two daughters of Caleb Barrows and his wife (whose name your writer cannot find). She called Caleb an early settler in Vassalboro; Henry Kingsbury, in his Kennebec County history, said he moved to Vassalboro from Camden in 1830.
Hanson Barrows spent his life on the farm he inherited from Caleb, named Twin Oaks, on Barrows Road (Kingsbury said the farm was “on the pond road,” probably meaning Webber Pond Road). In 1971, Robbins wrote, the Barrows family home still stood, with a view across the golf course to Webber Pond.
(Barrows Road ran west from Webber Pond Road to the section of Old Route 201 named Holman Day Road. On May 13, 2010, the Vassalboro select board ordered the road discontinued, without retaining a public right-of-way. Voters at the June 7, 2010, town meeting ratified the decision.)
Hanson Barrows and his wife, Julia E. (Wood) Barrows (1854-1942), are buried in Vassalboro’s Union cemetery. Their son, Leon Martell Barrows (Oct. 24, 1888 – March 5, 1956), in 1911 married Bertha May McCloud (1892-1913).
(Hanson’s brother Edwin [April 2, 1842 – April 20, 1918] was profiled in the article on Civil War veterans in the March 31, 2022, issue of The Town Line.)
* * * * * *

The Lombard house in Waterville, today, across from the public library. (photo by Roland Hallee)
Alvin Orlando Lombard was born June 15, 1856, in Springfield, Maine. Various sources say by the age of eight he was at work in the family mill – a shingle mill, in Lincoln, Maine, Smith wrote, where the “[s]toutly built, inquisitive, and energetic” boy “quickly mastered every woodland task from lumberjack to river driver and from stacker to mill sawyer.”
The child also built machines. Several sources mentioned his miniature water-powered sawmill (or wood-splitter – sources disagree) that he demonstrated by cutting up cucumbers.
Later, Lombard and his younger brother Samuel operated a blacksmith shop, in Waterville. Wikipedia said Alvin designed “sawmill and logging equipment” and Samuel supervised manufacturing.
Smith wrote that in the summer of 1899, Lombard, age 43 and already known as an inventor, shared a streetcar ride with his wealthy Fairfield friend, E. J. Lawrence. Lawrence “bemoaned the cost and cruelty” of using horses to haul harvested trees out of the Maine woods in the winter and asked Lombard if a machine could be used instead.
Two days later Lombard showed Lawrence a wooden model of a tracked vehicle. Lawrence liked it. The two built a full-size sample at Waterville Iron Works, “and on May 4, 1901, U. S. Patent #674,737 was issued for the Lombard Log Hauler, arguably the most significant invention ever to come from the State of Maine.”
Lombard’s machine was powered by “a steam engine with an upright boiler” and ran on steerable front skis and rear caterpillar treads. Here is Smith’s description: “A continuous belt of hinged steel lags (treads) was fitted over two pairs of geared wheels, allowing the heavy machine to pull itself along on a rolling carpet of steel…, like a caterpillar.”
These machines replaced “the work of 50 lumber-pulling horses,” one source said. Another called the log-hauler the model for “every snowmobile, tank and bulldozer ever built.” Even after trucks succeeded tractors in the Maine woods in the 1930s, the caterpillar tread continued to expand its uses world-wide.
The Maine Forest and Logging Museum website lists the six known Lombards remaining of the 83 built between 1900 and 1917. Two are at the museum in Bradley, the website says.
In addition to the log hauler for which he is best known, Smith wrote that Lombard’s commercially successful inventions included “a device for tossing (de-barking) pulpwood, and an apparatus that separated knots and sawdust from ground pulp.”
Smith said Lombard was most proud of an 1893 invention, “an automatic mechanical device…that maintained the speed and power of water turbines.” Lombard made and sold this useful regulator for six years before selling the patent and, according to Smith, dividing his time between his house in Waterville, where he had a basement workshop, and his country house in Vassalboro.
An online genealogy says Lombard and Mary Etta Bates (Sept. 8, 1856 – April 13, 1931) were married June 13, 1875, in Webster Plantation. They had one daughter, Grace Vivian Lombard Vose (Dec. 8, 1876-Aug. 24, 1947).
Alvin Lombard died Feb. 21, 1937. He, his wife and their daughter are buried in Waterville’s Pine Grove cemetery.
Online sources list two memorials to Lombard. Mount Lombard, in Antarctica, recognizes his contribution to driving over snow; and his Waterville house, now an apartment building, is on the National Register of Historic Places.
Your writer, and Vassalboro Historical Society president, Janice Clowes, add Lombard Dam, on Outlet Steam, in Vassalboro, recently removed to allowed alewives to migrate into China Lake, and Lombard Dam Road.
Who invented the snowmobile?
Earl Smith nominated O. C. Johnson, of Waterville, who, inspired by Alvin Lombard’s log hauler, “is said to have built one of the first snow machines in 1909. It was ten feet long and powered by a ‘one lung’ engine.”
Your writer failed to find additional information on O. C. Johnson. On-line sources say early versions of the snowmobile were invented in 1911 by Harold J. Kalenze, of Brandon, Manitoba, Canada; in 1915 by Ray H. Muscott, of Waters, Michigan; in 1917 by Virgil D. White, of Ossipee, New Hampshire; in 1922 (much improved by 1935) by Joseph-Armand Bombardier, of Valcourt, Québec, Canada; and in 1924 (patented in 1927) by Carl Eliason, of Sayner, Wisconsin.
A snowmobile history found on the Volo Museum’s website credits White, Eliason and Bombardier, and agrees with Smith. The website says: “One of the earliest snowmobile ancestors is the steam-powered Lombard Log Hauler….”
Appeal to our readers
An appeal to our readers, especially those in Windsor, to help an out-of-state historian.
Peter Pettingill, from Barrington, New Hampshire, is seeking local information on an event in Windsor that he described as “the death of Charles Northey, Jr., which occurred in South Windsor, in October, 1905, resulting in the sensational six-and-a-half-week trial of resident Alice Spencer Cooper.”
He added, “It was the longest trial in Maine’s history at the time and was in the press from Maine to California and involved countless folks from your area and a lot of prominent Maine characters.”
Mr. Pettingill has done a lot of on-line research; he visited the area this past summer to check out graveyards and remaining buildings. He would appreciate more information from local people – does anyone have an ancestor in the Northey or Cooper family, or perhaps one who was involved in the trial?
In 2022 he published Porter: The Murder of David Varney (your writer found favorable reviews on line). His second book, titled The Murder of Mattie Hackett, is due out by the end of the year, he said.
For anyone with relevant information, Mr. Pettingill’s email address is pettingillp@yahoo.com. His postal address is 58 Waterhouse Road, Barrington, NH 03825.
Main sources
Kingsbury, Henry D., ed., Illustrated History of Kennebec County Maine 1625-1892 (1892).
Lowden, Linwood H., good Land & fine Contrey but Poor roads a history of Windsor, Maine (1993).
Robbins, Alma Pierce, History of Vassalborough Maine 1771 1971 n.d. (1971).
Smith, Earl H., Downeast Genius: From Earmuffs to Motor Cars Maine Inventors Who Changed the World (2021).
Websites, miscellaneous.










 Residents of Fairfield may cast their ballots on Tuesday, November 7, 2023, at the Fairfield Community Center, 61 Water Street, Fairfield, from 8 a.m. to 8 p.m.
Residents of Fairfield may cast their ballots on Tuesday, November 7, 2023, at the Fairfield Community Center, 61 Water Street, Fairfield, from 8 a.m. to 8 p.m.


 Amaris Charland, of Fairfield, graduated with a Bachelor of Arts degree in Art from Blackburn College, in Carlinville, Illinois, during the institution’s 154th Commencement ceremony in May 2023.
Amaris Charland, of Fairfield, graduated with a Bachelor of Arts degree in Art from Blackburn College, in Carlinville, Illinois, during the institution’s 154th Commencement ceremony in May 2023.

