Public advocate applauds PUC decision to dismiss CMP’s five-year rate proposal
Maine Public Advocate Heather Sanborn has released the following statement commending the Public Utilities Commission (PUC) for dismissing Central Maine Power’s (CMP) proposed five-year rate plan, a filing that would have significantly increased electric distribution costs for Maine households beginning in 2026.
“The Public Utilities Commission made the right call today in dismissing CMP’s five-year rate proposal. At a time when thousands of Maine people are already struggling to afford their electric bills, CMP’s plan simply asked for far too much.
“While this decision prevents a deeply flawed proposal from moving forward right now, we know that CMP will have the opportunity to refile. In the meantime, we look forward to engaging with other stakeholders and the Commission in providing our utilities with guidance about designing a rate plan proposal that keeps affordability and improved performance as the central focus. The Office of the Public Advocate will scrutinize any future proposal to ensure that any increases are reasonable, necessary, and in the best interest of Maine consumers.
“The decision today reflects the fact that Mainers were very engaged and spoke out about the unaffordability of CMP’s proposal.”



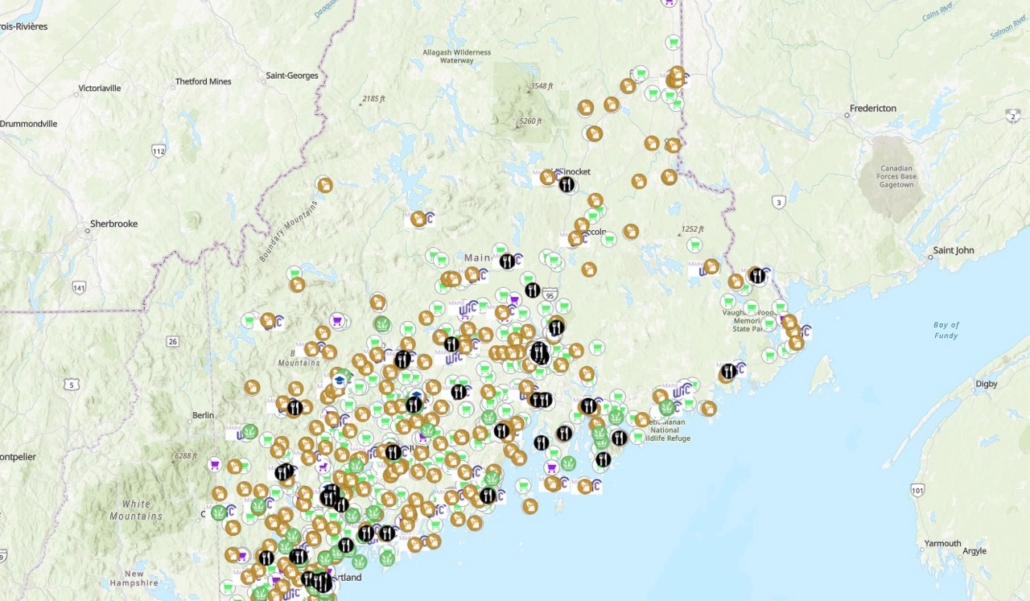 The Maine Department of Agriculture, Conservation and Forestry (DACF) today announced the launch of the Maine Food Access Map, a statewide interactive resource that helps individuals and families locate nearby food pantries, meal sites, school-based programs, WIC clinics, and other free or donation-based food assistance services.
The Maine Department of Agriculture, Conservation and Forestry (DACF) today announced the launch of the Maine Food Access Map, a statewide interactive resource that helps individuals and families locate nearby food pantries, meal sites, school-based programs, WIC clinics, and other free or donation-based food assistance services.
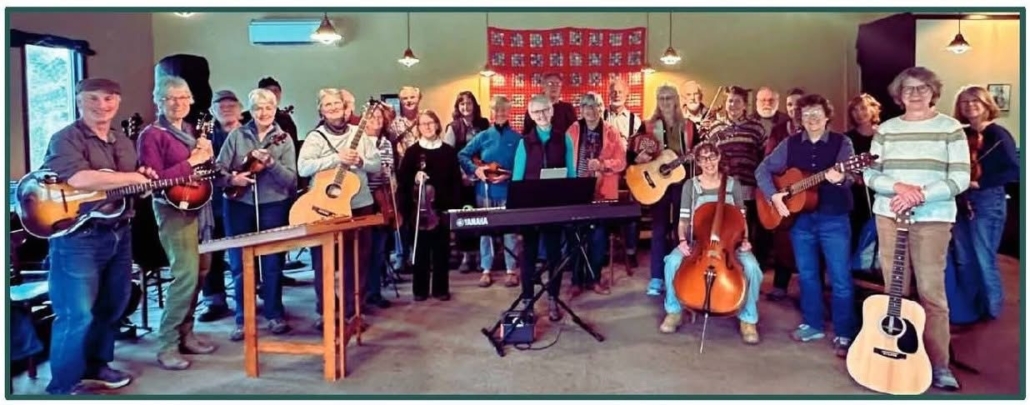 An afternoon of live music with the SeaStrings, a local group of friends and neighbors from mid-coast Maine, will be performed on Sunday, December 14, at 2 p.m., at the
An afternoon of live music with the SeaStrings, a local group of friends and neighbors from mid-coast Maine, will be performed on Sunday, December 14, at 2 p.m., at the 
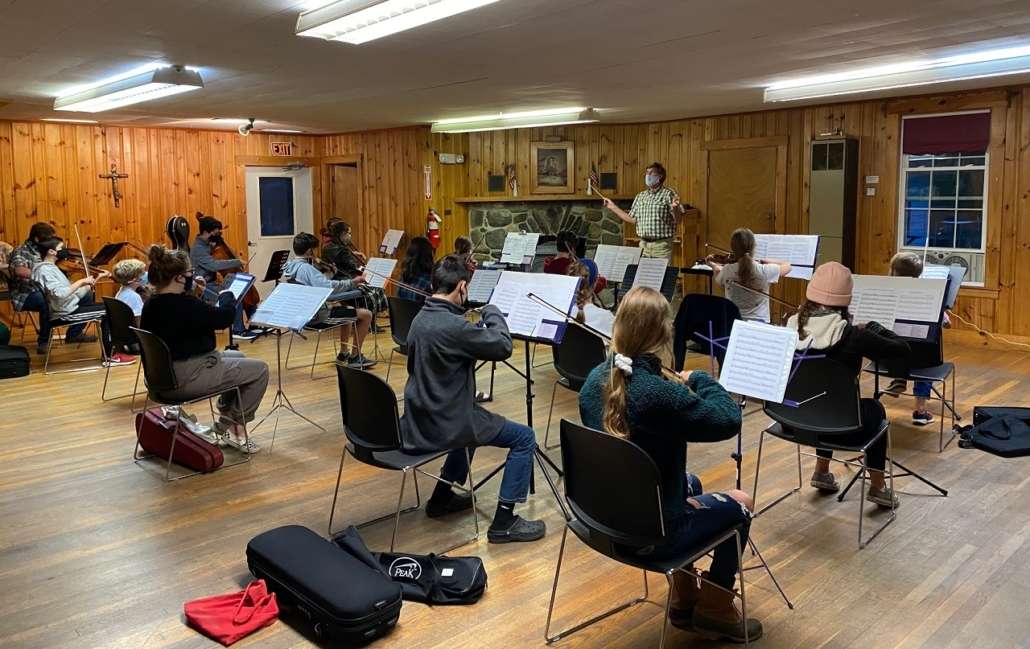
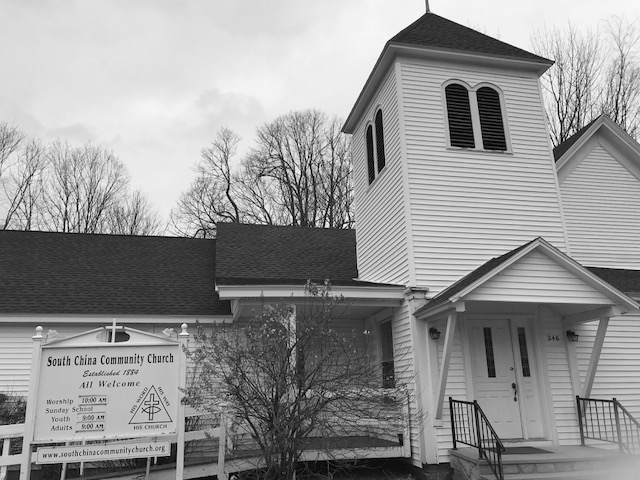

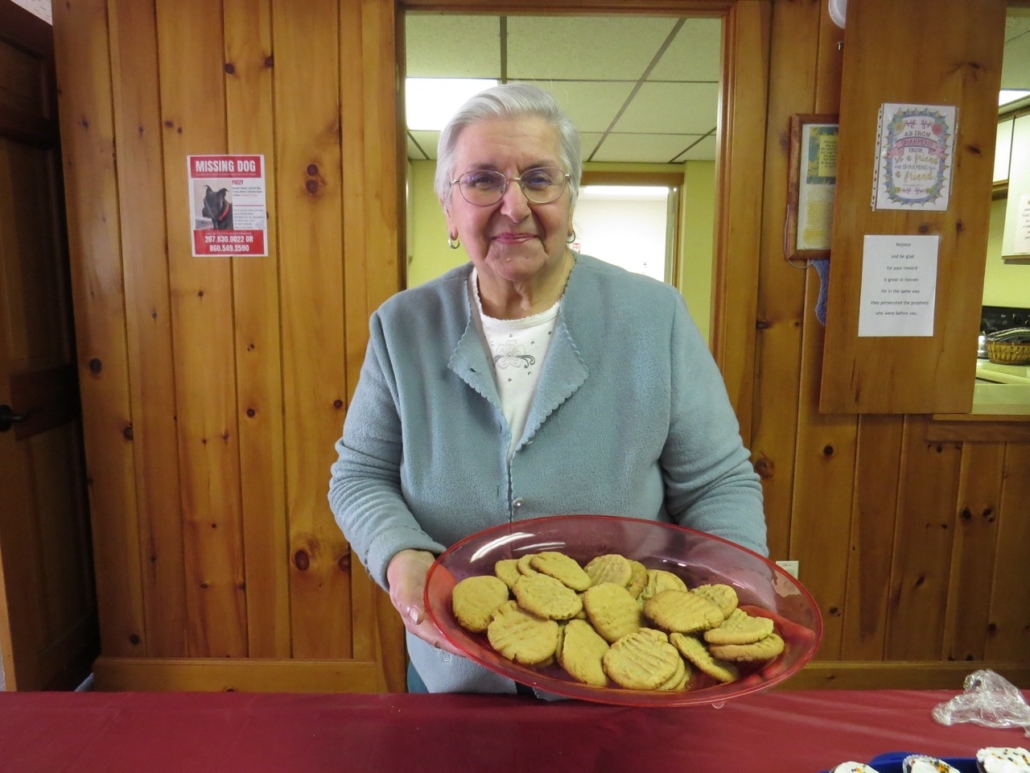
 Many thanks to everyone who helped make the Keyboard Dedication Service at South China Community Church (SCCC) on Friday, October 3 such a success – from those who provided the beautiful music to Pastor Paul to Susie Harwath (owner of “Susie’s Bakery”) and all who attended.
Many thanks to everyone who helped make the Keyboard Dedication Service at South China Community Church (SCCC) on Friday, October 3 such a success – from those who provided the beautiful music to Pastor Paul to Susie Harwath (owner of “Susie’s Bakery”) and all who attended.
