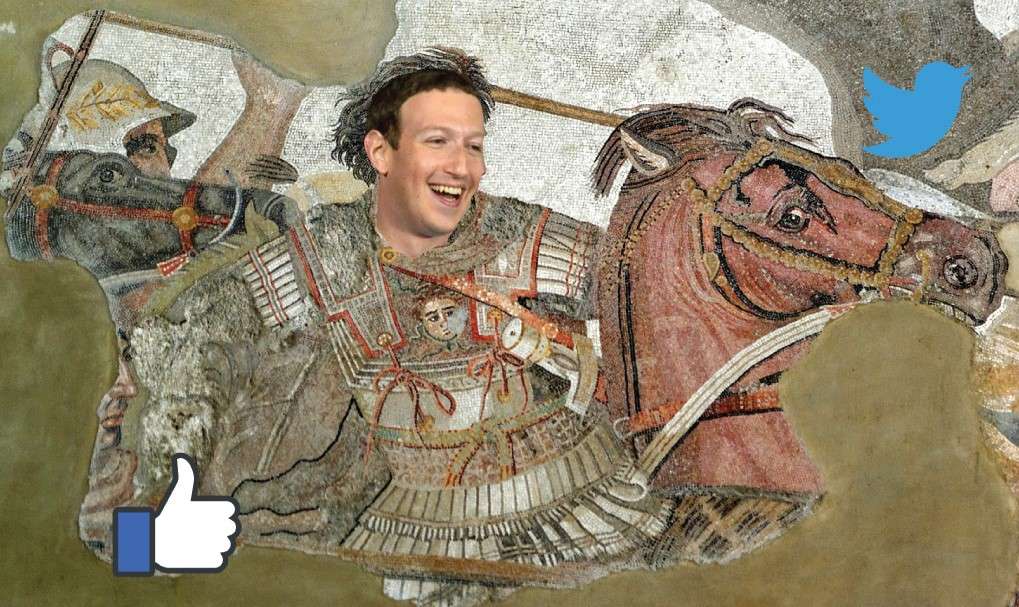
A mosaic depicting Alexander the Great in battle, discovered in the city of Pompeii, superimposed with the face of Mark Zuckerberg.
There is something in the philosophy of history variously called the Whig interpretation of history, Whig historiography, or just Whig history. It’s a view that sees the historical record as an inexorable push toward greater progress and civilization. In this view of the past, society is on a continuous path from savagery to civility, constantly improving, becoming freer, always taking two steps forward for any regrettable step back.
This idea gained popularity during the 18th century Enlightenment and was epitomized in the writings of German philosopher Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (1770–1831) and in works such as The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire by English historian Edward Gibbon, published in six volumes between 1776 and 1789. Other Enlightenment thinkers, like David Hume, criticized the approach, and it lost some favor in the aftermath of the horrors of World War I and II, but the Whig view of history is still held by many people today, even if they may not be aware of its history or what to call it. There is an almost intuitive acceptance of the idea in modern culture.
As a social philosophy, it served as a driving force in the civil rights movement of the 1960s, expressed most eloquently in a 1968 speech at the Washington National Cathedral by Martin Luther King, Jr., where he said, “We shall overcome because the arc of the moral universe is long but it bends toward justice.” More recently, former President Barack Obama alluded to this sentiment after the 2016 election, saying, “You know, the path this country has taken has never been a straight line. We zig and zag and sometimes we move in ways that some people think is forward and others think is moving back. And that’s OK.” We may zig and zag but, ultimately, we are moving forward.
I have long been fascinated with this idea of history as a progression, ultimately, toward improvement. There is something comforting about it, something hopeful. And something obvious too. In our modern world where technology is constantly improving and offering us additional benefits, it’s easy to fall into thinking that continuous progress is part of some immutable law of nature, that progress is inevitable.
In recent years, however, I have grown more skeptical of the idea. For one thing, we have to ask: progress for whom? We generally judge outcomes based on our own present circumstances — in other words, we see our history as “progress” because we are the outcome of that history. We are the product of a cultural progression that produced us. The winners write the history, and their descendants read that history and deem it “progress”. But was it progress from the perspective of the Native American tribes that were wiped out by the coming of Europeans? Did Christianity represent progress for the pagans of the 4th century Roman Empire who were watching their traditions being replaced and superseded by a new religion? We tend to view the past as progress because we are the end products of the winning side. A natural bias, perhaps. The more serious error comes when we use this view of the past to make assumptions about the future.
Often social change is driven by technological innovations, particularly advances in how we communicate. Think about the invention of writing as one of those advancements that transformed, over a thousand years, oral societies into written ones. We take writing for granted today, but at the time it was revolutionary. No longer did you need to trust someone else’s recollection of past events. Now you had a written record, essentially immutable and unchangeable, at least in theory. Agreements could be written down and later referred to as a way to settle disputes. History could be recorded and preserved for future generations.
Writing brought many benefits to society. Most importantly, the ability to reliably preserve knowledge allowed subsequent generations to more easily build on the progress of past generations. But writing also introduced new conflicts about who would control how that information was preserved. In many ways, writing imposed new cultural restrictions on the ordinary person who had grown up in an oral society. There was now an official version of a story, and any interpretation that differed from it could be judged “wrong”. Control over the historical narrative was now dictated by an elite group with the specialized skills required to read and write. Writing made culture more transportable, but it also made culture easier to police. Writing introduced new cultural gatekeepers and also new conflicts.
The Bible tells the story of the Tower of Babel (Genesis 11:1–9), in which an early society comes together to build a tower to reach the heavens. Seeing this act as the height of arrogance, God strikes the people with a confusion of languages, confounding their undertaking and, unable any longer to communicate, they scatter across the earth. While the story is probably an origin myth meant to explain why various peoples speak different languages, it contains an important truth about the power of communication in human endeavors.
The conquests of Alexander the Great in the 4th century BCE serve as a foil to the story of the Tower of Babel and illustrates how fundamental communication is to the evolution of culture. Alexander was the ruler of Macedon, a kingdom located north of the Greek peninsula. Although there was debate even at the time about whether Macedonians were considered Greek, there is no question that Alexander was a devotee of Greek culture. Influenced by his tutor, the famous Greek philosopher Aristotle, Alexander sought to spread Greek culture in the lands he conquered. By the time of his death in 323 BCE at the age of 32, his empire was one of the largest in history and included Greece, the Middle East, Northern Africa (Egypt), and stretched as far east as India.
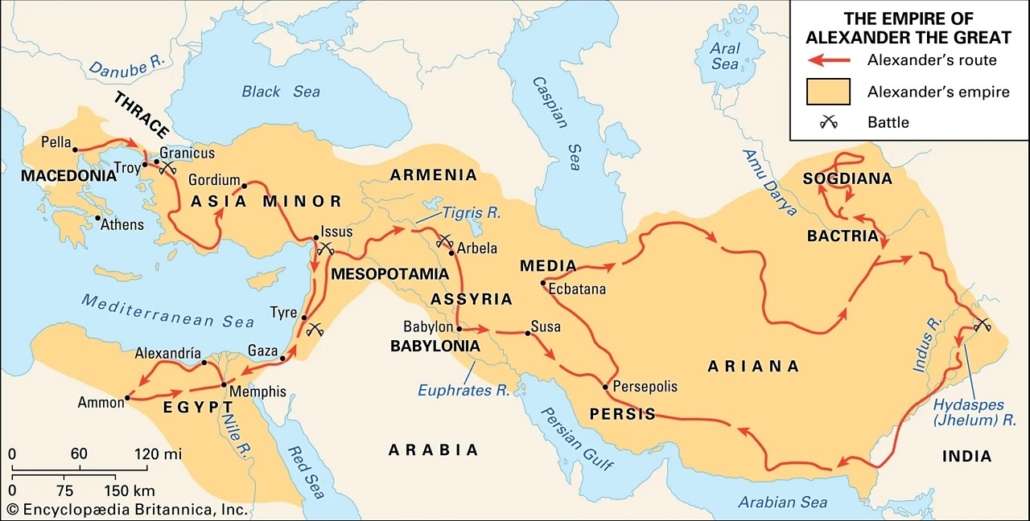
A map of the territory conquered by Alexander the Great. (photo credit: Encyclopedia Britannica)
But Alexander was not just a conqueror of territory, he was also a cultural evangelist. He was, by some reasonable estimates, the most influential figure in the history of Western civilization. During his short, 13-year military career, he founded dozens of cities (many named after himself) in the style of the Greek polis, or city-state of Ancient Greece. Most importantly, because of his influence, the Greek language became the lingua franca – the common language – for the entire region. Alexander the Great is the reason the New Testament was written in Greek. What God had torn asunder at the Tower of Babel, Alexander put back together again.
It’s important to note that while we may see this as progress now, and one of the foundational periods in the development of Western civilization, it was also an incredibly destructive process for the societies going through it. Greek culture replaced, or in many cases, merged with the existing native cultures to create a hybridized version in a process referred to by historians as Hellenization.
Rome later built upon the foundations that Alexander had laid down, although Roman culture was more about assimilation than innovation. Rome built the infrastructure, and through the Pax Romana (“Roman Peace”) created the stability that allowed Greek culture and ideas to flourish and spread in the centuries following Alexander’s conquests. Not only were Rome’s famous roads essential to the flow of goods throughout the empire, but also ideas, and ideas are the seeds of culture.
Aside from the invention of writing and the conquests of Alexander, the next most consequential advancement in human communication came in 1436 with the invention of the printing press. This changed the communication game in significant ways and kicked off a knowledge revolution that would lead to the Renaissance, the Protestant Reformation and eventually the Enlightenment, which introduced many of the ideas that have come to define modern society, including the scientific method of investigating the natural world and the “rights of man” which were enshrined in the American Constitution and the Bill of Rights.

An artist’s rendering of Johannes Gutenberg in his workshop.
By removing the human element from the copying process, the printing press both increased the accuracy of shared information and reduced its cost. As the cost of reproduction dropped, the written word became accessible to more ordinary people, which encouraged the spread of literacy in the general population. Ultimately, this led to the Protestant Reformation, with a large number of Christians breaking from the Roman Catholic Church. Christians could now read the Bible for themselves and no longer had to rely on those with special access to the written word for their interpretation. Martin Luther, the father of the Reformation, is alleged to have quipped, “Printing is the ultimate gift of God and the greatest one.”
The printing press removed many of the obstacles between the ordinary person and the written word and resulted in a proliferation of ideas, both good and bad. The witch hunting craze of the 16th and 17th centuries, during which an estimated 50,000 people, mostly older women, were executed on suspicion of practicing witchcraft, was in part fueled by the printing and widespread availability of one book, the Malleus Maleficarum, roughly translated as the Hammer of Witches, published in 1468 by two Catholic clergyman, Heinrich Kramer and Johann Sprenger. The book purported to teach readers how to identify a witch and turned many ordinary people into demonic detectives. The result: witch hunting hysteria. It’s hard to see this as anything other than a phenomenon inspired by the spread of literacy, combined with a highly-charged religious environment, in the decades after the introduction of the printing press.
Whether we’re talking about Roman roads, the printing press, or more recent inventions like the telephone, radio, television or the internet, social change is usually preceded by advancements in communication technology. But these advancements have often been a double-edged sword and are frequently accompanied by periods of heightened conflict, and an increased propensity for hysterical thinking in the general public. We treasure the opening words of the Declaration of Independence, but we can’t forget the brutality of the French Revolution, even though both were inspired by similar cultural ideals.
There are many parallels between the impact of the printing press on society and what we are seeing today with the internet. Like the printing press, the internet has eliminated obstacles between information and the average consumer. And like every other time this has happened, it’s leading to social upheaval as people adjust to the new information landscape. As in the past, people are asking, is this a good or a bad thing? Does this make society better or worse?
On one hand, the internet empowers those who previously had no power. It provides a platform for those who before had no voice. But, on the other hand, it enables the digital equivalent of witch burnings. Good information has never been so accessible, but wild theories also proliferate online and influence how people vote, how they make health decisions, and who they love or hate. People have access to all the information in the world, but do they have the wisdom to discern the good from the bad?
Is this what progress feels like? Do we zig zag through history but always move forward? Does giving people more access to information always benefit society? These are some of the questions that have been bouncing around my head in recent years. Will people 200 years from now look back on the social changes we are going through today and see it as progress? I think they will, but not because history inevitably marches towards something we can objectively label as “progress”. It will be because they are the end products of the cultural conflicts we are living through right now, and viewed from the destination, whatever path history takes you down will look like progress to those at the end of the race.
Contact the author at ericwaustin@gmail.com.
 by Roland D. Hallee
by Roland D. Hallee