Up and down the Kennebec Valley: Vassalboro dams
by Mary Grow
As last week’s article on the Masse family suggested, from the late 1700s through the 1800s central Kennebec Valley entrepreneurs dammed streams and rivers to provide water power for industry.
Local histories have long lists of dams on streams tributary to the Kennebec River, before people got up the courage to try to control the river itself. Falling water managed by dams and waterwheels provided power, especially for sawmills to convert trees into lumber and grist mills to grind grain into flour.
One website dates grist mills to the first century B. C. Here is an explanation of an American grist mill, mostly from a Texas website:
The mill workings consist of two large stones, one atop the other. One source said four feet in diameter was a common size. The bottom stone, or bed stone, is fixed; the top stone, or runner stone, “rotates on top of the bed stone.” The runner stone has a hole in the top where grain is poured in to be “ground between the two stones.”
Wikipedia says the Romans built water-powered sawmills in the third century A.D. In the Nov. 2 issue of The Town Line, readers learned about the transition in Kennebec Valley sawmills from early up-and-down saws to the more efficient circular saw that William Kendall, Jr., of Fairfield, invented around 1827.
Outlet Stream, which runs from China Lake to the Sebasticook River (which flows into the Kennebec River in Winslow), was an example of a power source. The villages at East Vassalboro and North Vassalboro were established primarily because water power was available.
Your writer found no date for the China Lake Outlet Dam, in East Vassalboro. Henry Kingsbury, in his Kennebec County history, described it as a manufacturing hub. John Mower had an (undated) bark mill on the east end; his father, Nathan Mower, and another man named Thomas Sewall ran nearby tanneries; and on the west bank was “Thomas Greenlow’s shop, with its four forges and trip-hammers run by water.”
The Vassalboro Woolen Company, owner of North Vassalboro’s major mill, bought the outlet dam in 1872, so it could control the flow of water to accommodate its mills. The company donated it to the Town of Vassalboro in 1961, according to Herman Masse’s 1977 History of the Old Water Power Grist and Saw Mill.
The Masse mills in East Vassalboro, introduced last week, were not the first on the stream: Kingsbury said East Vassalboro village had a water-powered sawmill before its first houses. He wrote that the original landowners, the Kennebec Proprietors, “probably were instrumental in the erection of the first saw mill here, a few rods below the village bridge, before this portion of their territory was settled.”
Vassalboro was settled around 1760, and Masse’s history says the town had 10 families in 1768, so this first mill must have been in operation before the American Revolution.
Here a succession of owners cut boards for settlers’ houses and to ship down the Kennebec to sell, according to Kingsbury. Later a tannery (for making animal hides into leather) succeeded the sawmill, operating into the 1870s.
Downstream from this mill, Kingsbury wrote, were another sawmill, still operating in 1892, and a grist mill with a stone bottom story (these were the mills the Masse family acquired); and farther downstream, “but within East Vassalboro,” another grist mill.
The East Vassalboro Grist and Saw mill, a/k/a the Masse mill, was owned by Herman Masse when it was added to the National Register of Historic Places in January 1982. The Maine State Historic Preservation Commission’s October 1980 application was prepared by historian Frank A. Beard and architectural historian Robert L. Bradley.
They wrote, “The East Vassalboro Grist and Saw mill may well be the oldest mill site in Maine continuously operating in its original buildings and still using water power exclusively for the generation of energy.”
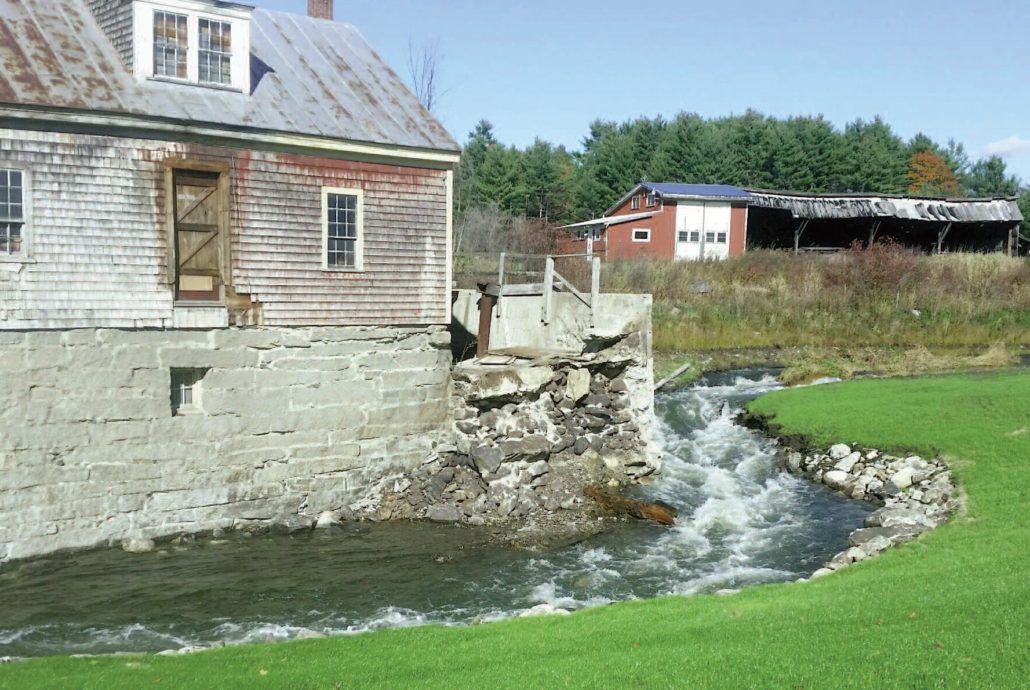
The property consisted of two buildings on either side of a dam across Outlet Stream, on the east side of Route 32 toward the north end of East Vassalboro. Outlet Stream runs generally north-south; but just upstream of the Masse dam site it turns sharp left (west), so it runs briefly from east to west. Masse’s two mills were on the north and south banks, the grist mill on the north and the sawmill on the south.
The application provided historical information, most taken from Herman Masse’s 1977 history. Additionally, Stephen Robbins shared with your writer a history of the mill as described by his cousin, Donald Robbins, in a 2015 presentation to the Vassalboro Historical Society.
Donald Robbins said that in 1797, John Getchell deeded half the water rights and 1.5 acres of land to Nathan Breed for a sawmill. Herman Masse added that Getchell reserved the right to build a grist mill and specified that his mill would have preference over Breed’s mill for water rights.
The Historic Preservation application credits Getchell with building the sawmill in 1798, “about 300 yards above its present location,” or, Masse wrote, about where the East Vassalboro Grange Hall now stands. It was described as a story and a half post and beam building, with a gable roof and attached sheds on the east and north.
Both sources say Jabez Dow built the grist mill, in or maybe after 1805. Beard and Bradley wrote that the sawmill was moved to face it across the stream.
The grist mill was also post and beam, story and a half, gable roofed, with one attached shed. The state historians wrote: “The most distinctive feature of the grist mill is its cut granite foundation walls which on the rear (west side) of the building are exposed and fitted with a door and four windows.”
The grist mill was “owned by retired ship captains” – Herman Masse’s history said several from Nantucket moved to Vassalboro in 1827 — and “operated, but not owned” by Zachariah Butterfield after 1812. Jacob Butterfield ran the sawmill, and handed it down to his son, Henry Rice Butterfield. The state preservationists could not determine how these two Butterfields were related to Zachariah.
In her 1971 Vassalboro history, Alma Pierce Robbins listed a dozen Nantucketers, most of them Quakers, who settled in Vassalboro. They came, she explained, because they knew the area from trips to the Kennebec to buy lumber to build their houses on Nantucket. Some planned to continue “shipping and shipbuilding” on the river; others were ready to try farming.
The Vassalboro Woolen Company bought both these mills and all water rights in 1872 “in order to control the flowage.” Warren Seward or Seaward leased the sawmill from 1872 to 1890.
The 1879 map of the village, reproduced as part of Donald Robbins’ presentation, shows a large mill pond along the east side of East Vassalboro, behind the houses lining Main Street.
In 1890, Robbins said, Seward bought his mill and half the water rights from Vassalboro Woolen, and Josiah Evans bought the grist mill and the other half of the water rights. After arguing over who should contribute what to dam maintenance, in 1912 they both sold to Louis Masse. From Louis Masse the properties went to his son Herman in the 1920s and then to Herman’s son Kenneth.
In the 1920s, Herman Masse wrote, lumbermen dumped logs into China Lake, where they were gathered inside a chain boom and towed to the Outlet Dam and thence into the mill pond on their way to the mill. It took about two days to bring a boom from South China to East Vassalboro, he said.
After describing some of the 20th-century improvements and updates the Masses made, Donald Robbins’ presentation ends, sadly, with photos from 2010, 2011 and 2015 showing crumbling stone, rotting wood and other deterioration. He mentioned a granite wall that partly collapsed in 2009-2010, damaging a water company pipe, and a floor that rotted out and fell into Outlet Stream in 2015.
In 2016 the buildings and the dam were removed as part of the program to restore alewives to China Lake, and also to protect the water company (see the article by Landis Hudson of American Rivers in the July 14, 2016, issue of The Town Line, available on line).
* * * * * *
Stephen Robbins directed your writer to an on-line copy of the 1869 water sites report, which describes 13 dams and dam sites for the lower part of Outlet Stream, from East Vassalboro through Winslow to the Sebasticook River.
Information was based on a report by Ira E. Getchell, Esquire, of Winslow, and “the Statement of the Selectmen.” Since the dams are listed under Vassalboro, though some are in Winslow, your writer assumes the Vassalboro selectmen made the statement.
The first dam was 120 rods (one rod is 1/320 of a mile, so 120 rods is a bit over a third of a mile) below Outlet Dam, owned by Vassalboro Mills Company and powering a woollen (the report’s spelling) and grist mill “when in operation.” H. R. Butterfield was using surplus water for a sawmill and “shovel handle factory.” He apparently inherited the latter, at least, from his father, because the 1850 census copied in Alma Robbins’ Vassalboro history lists Jacob Butterfield as a maker of shovel handles.
(When Alma Robbins wrote, “In 1833 the shovel handle factory burned,” she must have been referring to an earlier shovel handle factory; where it was, she gave no clue.)
Dam number two, another 120 rods downstream, powered Butterfield’s grist mill. (This was probably what was in the 21st century the Morneau dam, or a predecessor nearby.)
Number three, 200 rods (a little over 0.6 miles) downstream, powered a “shingle mill, wood and iron machine shop” owned by Charles Davies. (Probably the Lombard dam.)
The fourth dam site, immediately below the Davies’ dam, was undeveloped.
Another 440 rods (more than a mile and third) downstream were the dam and canal where the Vassalboro Mills Company made woolen goods and had a wood and iron machine shop and other facilities. This dam, in North Vassalboro, seems to have generated the most power of any on Outlet Stream.
(The history of the North Vassalboro mills is too long to compress into this week’s remaining space. Please see next week’s issue.)
Number six on the 1869 list was “an unoccupied stone dam” beside the canal. (Modern names for North Vassalboro’s dams were Box Mills and Ladd.)
The dams along this stretch of stream were untypical, in that they survived – not all intact and functioning, but visible and with names – into the 21st century.
In the last decade, the Masse, Morneau and Lombard dams have been removed. At Box Mills, Ladd and Outlet dams, fish ladders have been installed to allow migratory fish to reach China Lake from the Atlantic Ocean, via the Kennebec and Sebasticook rivers.
Main sources
Beard, Frank A., and Robert L. Bradley, National Register of Historic Places Inventory – Nomination Form, East Vassalboro Grist and Saw Mill (October 1980).
Kingsbury, Henry D., ed., Illustrated History of Kennebec County Maine 1625-1892 (1892).
Masse, Herman C., History of the old water power grist and saw mill at East Vassalboro, Maine, 1797-1971 : owned and operated by the Masse family since 1912 (1977).
Robbins, Alma Pierce, History of Vassalborough Maine 1771 1971 n.d. (1971).
Robbins, Stephen, Personal correspondence.
Websites, miscellaneous.
* * * * * *
CORRECTION
In the November 23, 2023, issue, Kennebec Valley History, on page 10, in the third column, sixth paragraph, it should have read: “Robbins dates the mill complex to 1797.”