Up and down the Kennebec Valley: Winslow, Hollingsworth & Whitney
by Mary Grow
In addition to the historic mills on Outlet Stream and smaller flowages in Winslow, Kingsbury mentioned two larger mills on the east bank of the Kennebec in the 1890s.
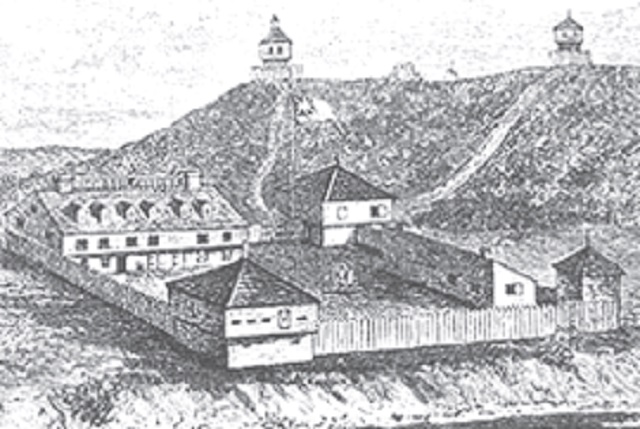
One he described as a new “large steam saw mill…on the historic grounds of Fort Point,” covering most of the “palisade enclosure of old Fort Halifax.”
Old Fort Halifax was built in 1754 to deter the French and their Indian allies from attacking British settlements along the Kennebec River. After the ouster of the French from the area in 1763, the fort’s buildings were dismantled or allowed to fall down, until only one blockhouse survives, now the centerpiece of Winslow’s Fort Halifax Park. (See the Jan. 28, 2021, issue of The Town Line for more on this historic site.)

A deteriorating blockhouse at Fort Halifax, in Winslow, after the ouster of the French from the area in 1763.
The grounds went through a succession of owners and uses. The Maine Memory Network’s on-line site includes an item donated by the Winslow Historical Preservation Committee with an excerpt from the April 18, 1873, Waterville Mail commending an effort to preserve the remaining blockhouse, after “many years of talk and neglect.”
The Ticonic Water Power Co. then owned the buildings and had leased them to “Dr. Crosby” of Waterville and “J.W. Bassett and A.T. Shurtleff, of Winslow, for the purpose of preservation.”
Another on-line source says the Ticonic Water Power and Manufacturing Company was incorporated in 1868 and “acquired the water rights and property adjacent to the Ticonic Falls.” In 1874, the Ticonic Power Company “became the Lockwood Company.”
The Lockwood Company is primarily associated with the mills in Waterville, just south of Ticonic Bridge. However, an on-line history of these mills says that in 1865, Waterville resident George Alfred “achieved the complex task of assembling water and property rights on both sides of the Kennebec River” in Winslow and Waterville.
Ownership of water rights let Alfred build a dam at Ticonic Falls, finished in 1869, the site says. It goes on to discuss the Waterville mills, built by Amos D. Lockwood, an engineer from Boston and Providence, who was familiar with water power.
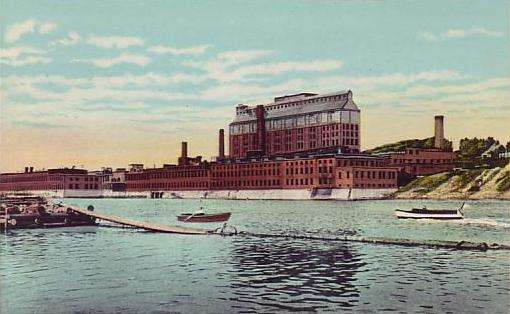
On the Winslow side of the river, Kingsbury wrote that Edward Ware leased the land on Fort Point from the Lockwood Company and built a lumber mill in 1890. The building was more than 300 feet long, equipped with “all modern appliances for cutting lumber,” Kingsbury wrote. Logs came down the Kennebec from up-river timber operations and were made into lumber, shingles and lath, mostly shipped to Boston.
Your writer found the beginning (only) of a New York Times article on line, headlined “Lumber Ordered for Gray Gables,” with the dateline Boston, Sept. 30 (no year given). The first sentence reads: “Twenty-five thousand feet of spruce lumber has been ordered to be shipped from the sawmill of Edward Ware, at Winslow, Me.”
Gray Gables, Wikipedia says, was an elaborate house in Bourne, Massachusetts, built in 1880 and in 1890 bought by past and future president Grover Cleveland. He named it Gray Gables and used it as the summer White House during his second term, 1893-1896.
* * * * * *
The second large Winslow mill was under construction as Kingsbury finished his history in 1892. He wrote that Hollingsworth and Whitney was building Kennebec County’s “largest pulp and paper mill…on the east bank of the Kennebec, at a cost of three quarters of a million dollars.”
The University of Maine’s on-line Digital Commons provides a history of Hollingsworth and Whitney, written in October 1954 by company president James Lester Madden as the company merged into Scott Paper Company.
Madden wrote that the first Hollingsworth in the paper business was Mark Hollingsworth, from Delaware, who started in 1798 as a foreman in a Massachusetts mill.
In 1835, Hollingsworth bought a Revere Copper mill in South Braintree, Massachusetts, and converted it to a paper mill that was run until 1852 by his sons, John and Lyman. In 1852, another son, Ellis, came home after three years in California and took over the South Braintree mill.
In 1862, Ellis Hollingsworth formed a partnership with Leonard A. Whitney, Jr., owner of a “paper mill and bag factory” in Watertown. Whitney’s factory, Madden said, “produced the first machine-made paper bags in this country.”
Hollingsworth and Whitney’s first Maine venture was the purchase of a mill in Gardiner in 1876. Ellis’s son Sumner Hollingsworth was in charge.
In 1875 the company hired a “dynamic” sales manager named Charles Dean. After both founders died in 1881, Dean “was instrumental in incorporating the present [1954] company in 1882.” Sumner Hollingsworth was its president until his death in 1899, when Dean succeeded him and headed the company until he retired in 1911.
Hollingsworth and Dean had the Winslow mill built between 1891 and 1893, Madden wrote. He commented, “To move from Massachusetts to the wilds of Maine for a woodpulp and paper mill was a daring move in the 1890s.”
The original estimated cost turned out to be half the actual cost of $800,000, he said (see Kingsbury’s figure above). Because the 1893 financial panic made banks hesitant to lend, even to a company with a good record, Dean financed part of the building himself. The Winslow mill was “a high quality, very low cost producer,” and he was soon repaid from profits.
The mill had two paper machines and a pulp mill; its daily capacity was 30 tons of groundwood pulp and 20 tons of paper. Madden said the initial 150 employees worked 11- and 13-hour days for an average hourly wage of less than 15 cents.
“Under Mr. Dean’s leadership,” Hollingsworth and Whitney was the first paper company to go from two to three shifts, a change that was considered “very radical,” Madden wrote.
To guarantee a supply of wood, the company began buying forest land in 1895. By 1954, Madden said, it owned 550,000 acres in the Kennebec watershed.
He described additions and improvements at the Winslow mill in the first two decades of the 20th century (the last two paper machines were added in 1913 and 1916) and the building of a pulp mill in Madison, and praised the company’s products and reputation.
Madden said nothing about World War I. By World War II, he wrote, the Winslow mill was the only supplier of “Tabulating Cardstock” in the country. Production was quadrupled to meet the military’s need for “cards to operate tabulating machines.”
After Scott Paper sold to Kimberly-Clark, the Winslow mill was closed in 1997.
* * * * * *
Kingsbury listed another 10 mills on lesser streams and brooks in Winslow before 1892.
Again, a map of Winslow is helpful. As explained last week, the town is bounded on the west by the Kennebec River. On the south it is bordered by Vassalboro, on the east by China.
There are two ponds in Winslow. The smaller, Mud Pond, is in the southeastern corner of town, with its eastern shore in China (according to China tax maps and most others found on line; one on-line map shows the boundary deviating from a straight line to follow the shoreline, putting the whole pond in Winslow).
A connecting stream runs northwest from Mud Pond to larger Pattee (or Pattees or Pattee’s) Pond, which lies east of the Sebasticook River. The Pattee Pond outlet stream, and streams that join it from the east, drain northwest into the Sebasticook.
In addition to the streams associated with these two water bodies, contemporary maps show one stream, Chaffee Brook, flowing west into the Kennebec. Chaffee Brook passes under Route 201 a short distance south of the Carter Memorial Drive intersection.
The first dam Kingsbury mentioned was on the brook named for John Drummond “near the river road” (Route 201).
Your writer found no Drummond Brook in contemporary Winslow; she guesses Drummond Brook is now Chaffee Brook. Just north of Chaffee Brook, Chaffee Brook Road goes west off Route 201 to the bank of the Kennebec. On the south side of Chaffee Brook Road sits Drummond cemetery.
(Chaffee Brook Road leads to the Kennebec Water District’s Chaffee Brook pumping station, which is being upgraded. Area residents who have seen the crane on the river bank and the platforms in the water are looking at the project.)
Drummond built a grist mill with two runs of stones, Kingsbury said. In 1822 he sold it to Josiah Hayden (probably the younger of the two Josiah Haydens in last week’s article) and built a sawmill (presumably sharing the grist mill’s water power). Kingsbury said as forests were cleared, the flow in this brook diminished until it could not provide adequate power after about 1840.
Of the next mill he described, Kingsbury wrote: “Frederick Paine had a plaster mill on Clover brook that did business from 1820 to 1870.” (On-line sources say plaster mills ground lime and gypsum into powder for building materials, including plaster and cement.)
Your writer suggests Clover Brook might be the 19th-century name for Bellows Stream, which flows north into Pattee Pond roughly parallel to the Kennebec and about midway between Winslow’s east and west boundaries.
The apparently nameless stream between Mud Pond and Pattee Pond, eastward of Bellows Stream, powered two mills, presumably on dams, by the first half of the 1800s. This stream flows north and then northwest from the north end of Mud Pond, under Route 137 (China Road) into the east side of Pattee Pond
The upstream mill was John Getchell’s sawmill, operating by 1795. It later became Isaac Dow’s shingle mill.
Half a mile downstream, a man named Alden had a sawmill that “ran down and was rebuilt by Esquire Brackett, who lost his life in it in 1840, by a blow from the saw frame.” Later, Jacob Brimner ran the sawmill (the 1856 map of Kennebec County shows a sawmill on this stream and a Brimner house not far upstream). Later still, a shingle mill ran until around 1870, Kingsbury said.
The Pattee Pond outlet, Pattee Stream, flows from the north end of the pond into the Sebasticook. For lack of space, your writer postpones a description of mills in this northern and northwestern part of Winslow to next week.
Main sources
Kingsbury, Henry D., ed., Illustrated History of Kennebec County Maine 1625-1892 (1892).
Websites, miscellaneous.