Up and down the Kennebec Valley: Natural resources – Part 1
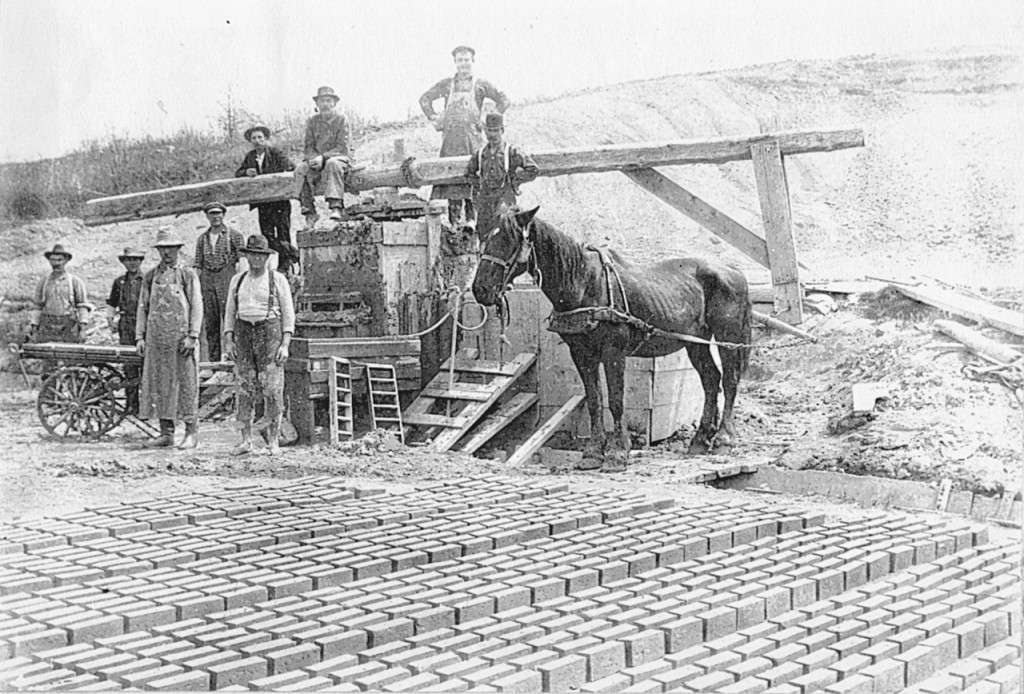
Brick making operation in Brewer.
by Mary Grow
As the preceding articles have at least partly shown, pre-European inhabitants of the Kennebec Valley lived off the land, using natural resources to provide food, shelter, clothing, transport, decoration and other necessities and frivolities.
The first Europeans, arriving in small (by our standards) ships, had no choice but to imitate the Native Americans. They got food by hunting and fishing, built wooden shelters and grew crops suited to local conditions. However, they quickly branched out in two directions, monetizing many natural resources and adding imported and manufactured items.
Monetizing applied to wild animals, notably the sale of beaver and other furs to European traders; to fish, especially migratory species, a trade being revived in the 21st century; to forests, as land was cleared not only for houses and farms but for a lumber industry that covered much of Maine and continues today; and even to the ice that formed in the Kennebec River every winter and was exported globally (see the article on lumber driving and ice harvesting on the Kennebec in the May 14, 2020, issue of The Town Line).
The Kennebec Valley offered other natural resources that Europeans developed. Linwood Lowden, in his history of Windsor, mentions one of the most common: rocks.
After a would-be farmer in the Kennebec Valley cut down trees, hauled away the wood and dug out the stumps, he was usually left with a field full of rocks. Nuisances, yes, but, Lowden points out, useful: big ones were “drilled, split and removed to be used as foundation stones.” Smaller ones lined cellars and wells or made stone walls as field or property boundaries.
Some, Lowden wrote, were immoveable: the farmer and his friends would dig a hole and bury such problem stones. Smaller ones that continued to surface as the fields were plowed went to the “stone dump,” the otherwise unused area in some corner on every farm.
* * * * * *
The invaluable USM Digital Commons on line includes Mining in Maine: Past, Present, and Future, published in 1990 by Carolyn A. Lepage and others. This source considers granite, limestone, slate, feldspar and iron among Maine’s commercially important minerals.
In 1836, the Maine legislature hired a Bostonian named Charles Jackson to survey the state’s mineral resources. Lepage wrote that he inspected mostly coastal areas and “major river and overland routes.” From this sample, he concluded Maine minerals were worth developing.
By 1836, Lepage wrote, Maine was already an international granite exporter. Hallowell was one of five granite centers (plus Biddeford, Blue Hill, Penobscot Bay and Washington County).
The rest of the 19th century featured continued exploitation of resources, especially along the coast, and a brief period of excitement about gold, silver and other metals after the Civil War (with no indication that the Kennebec Valley was involved). Granite remained important; in 1901, Lepage wrote, the value of granite produced in Maine exceeded that from any other state. Maine’s granite industry slowly declined in the 20th century, especially during and after the Great Depression of 1929-1939.
A Maine Geological Survey website emphasizes slate, used especially for roofing tiles, as another important mineral. This site mentions the “Central Maine Slate Belt” that runs from the Waterville area more than 70 miles northeast to Brownville Junction.
* * * * * *
Another natural resource common enough to be mentioned in many town histories is clay.
Clay, Wikipedia says, is a fine-grained soil that contains clay minerals. Clay minerals, according to the same source, are “hydrous aluminium phyllosilicate minerals, composed of aluminium and silicon ions bonded into tiny, thin plates by interconnecting oxygen and hydroxide ions.”
These minerals are plastic – they stick together and are flexible – when they’re wet, but become rigid when they dry. The material can thus be made into many things, from bricks for walls to dishes for the people inside the walls to eat from.
Wikipedia provides more scientific information, including noting that clay is commonly found where water bodies, like glacial lakes, let the soil settle to the bottom. Since much of Maine was once under a glacier, the prevalence of clay is to be expected.
An on-line source says Maine clay is not particularly suitable for ceramics, but is excellent for brick-making. Residents exploited clay deposits for building materials, for houses and for larger structures like mills and public buildings.
The all-brick Besse Building, in Albion.
In Albion, Ruby Crosby Wiggin’s history described a brickyard on the shore of Fifteen-Mile Stream, across from the Crosby sawmill (built in 1810 and operated into the 1880s). When George Crosby built the Crosby mansion in 1886 (see the June 11, 2020, issue of The Town Line for more on the stream and the Crosbys), he used bricks from the brickyard.
Wiggin listed specific uses: three chimneys, “a large brick oven and water heater in the kitchen,” “a large tank in the cellar which was used for the liming of eggs” and brick paving for the section of the cellar floor used to store potatoes. (Storing fresh eggs in a mixture of water and lime in a cool place was one of several ways to keep them edible before refrigeration.)
The front wall of the wooden ell added to the mansion in 1832 had a brick facing, Wiggin wrote. After part of it collapsed into the driveway some 50 years later, the remaining bricks were replaced with clapboards.
Wiggin mentioned another brickyard at Puddle Dock, in southern Albion, and yet another “along the clay flat beside Alder brook.” From the later, allegedly, came bricks used to build a brick schoolhouse.
This building was the town’s District 4 schoolhouse, shown on the 1856 Kennebec County map on the north side of what is now Route 202, opposite the north end of Quaker Hill Road. Wiggin quoted Henry Taylor’s memory of his father’s description of the building as “a brick schoolhouse with a wooden clock on the outside denoting the time, quarter to nine.”
No one seemed to know what significance, if any, that particular time held. A new District 4 schoolhouse off Quaker Hill Road was built around 1858, Wiggin wrote. She did not say whether any others of Albion’s 20 or so school buildings were brick, nor did she list owners of any of the brickyards.
The 1913 brick Besse building was originally Albion’s high school and now houses its town office (it is briefly mentioned in the Sept. 30, 2021, issue of The Town Line).
In China, various sources say there were at least three brickyards, along the north end of the east basin of China Lake; there might have been seven in the town, according to the bicentennial history.
The history describes how clay was turned into bricks. It was “shoveled into a circular pond; water was added; and the mixture was stirred with a long sweep propelled by a horse walking around the pond.” The resulting goop was put into a “hand-operated moulding machine” that could make six bricks simultaneously. The bricks were sun-dried and then kiln-baked.
Captain Nathaniel Spratt started his brickyard on the stream then called Wiggin Brook, which runs into the west side of China Lake’s east basin a short distance south of China Village, in the 1820s or early 1830s, according to Henry Kingsbury’s Kennebec County history. He ran it for 25 years; the bicentennial history says that in October 1834 he advertised in the China Village newspaper, the Orb, that he had 230,000 bricks for sale. Later owners were Samuel Benson and Zalmuna Washburn. The brickyard went out of business in 1865.
(The bicentennial history explains that two early Wiggin Brooks were named for the Wiggin [or Wiggins] family of early settlers, which included two Nathaniels, father and son, one of whom fathered 25 children. The west-side Wiggin Brook, later Broad’s Brook, flows under Neck Road; Kingsbury associates “Hollis Broad’s widow” with the Spratt brickyard. The other Wiggin Brook, now commonly Meadow Brook [or Hunter Brook or Starkey Brook] is larger and flows into the east side of the muldoon [swamp] at the head of the lake.)
There are numerous handsome brick houses along Neck Road, including one just north of the former Wiggin/Broad’s Brook.
On the east side of the head of the lake, the bicentennial history says Abraham Talbot, a former slave, operated a brickyard. The town comprehensive plan dates it tentatively to the 1790s (see the June 23, 2022, issue of The Town Line for more information on the Talbot family).
Neither Kingsbury nor the bicentennial history gives a name or location for a third brickyard.
One significant brick building in China Village was the double store on the west side of the south end of Main Street, facing east down Causeway Street toward the end of the lake. Built around 1825 by two residents, Alfred Marshall (the northern two-thirds) and Benjamin Libby (the southern third), it housed various stores and intermittently the local Masonic chapter, with the two sections changing ownership separately.
The Masons briefly owned the whole building in 1866, but they promptly sold the north section. In 1919 they reacquired that part; the entire building was the China Village Masonic Hall until 2006, when the organization finished building a new hall on the east side of Main Street and had the old building demolished.
The Fairfield Historical Society’s 1988 bicentennial history says nothing about brickyards, but it and other sources describe many significant buildings made of brick.
One of the earliest was William and Abigail (Chase) Kendall’s house, built in the 1790s at the intersection of Lawrence Avenue and Newhall Street, a block west of the downtown area that was for years called Kendall’s Mills. The history says the building later housed Bunker’s Seminary, founded about 1857 (see the Oct. 21, 2021, issue of “The Town Line); it served “as a Masonic Lodge and as a boarding house” before it was demolished in the 1890s.
An on-line history says that “The United Boxboard and Paper Company, a three story brick mill complex, was established in 1882 at the northern tip of Mill Island.” (Mill Island is the largest and westernmost of the islands in the Kennebec between Fairfield and Benton.)
This mill provided pulp for paper-making at “the company’s other paper mill at Benton Falls and the Hollingsworth and Whitney Company (later Scott Paper) in Winslow.” The northern end of the island is now the town-owned Mill Island Park, designed by Waterville dentist Steve Kierstead, with walking trails built by the town public works crew and remains of the mill foundations visible here and there.
On Aug. 21, 1883, the bicentennial history says, some of wooden commercial buildings on Main Street burned down. The writers surmise that the fire probably “stimulated the building of the first of the brick blocks” on the street.
The most elaborate downtown brick building is the former Gerald Hotel, opened on June 4, 1900. Designed by Lewiston architect William R. Miller (1866-1929) for Fairfield business magnate Amos Gerald (1841-1913), it is described as “a striking Renaissance Revival structure, with a sophistication of design and decoration not normally found in rural Maine.” The building served as a hotel until 1937, according to the history, and was considered “the most elegant, if not the largest” in New England.
After 1937 the building was for many years home to Northern Mattress and Furniture Company. It has been listed on the National Register of Historic Places since 2013.
The original Lawrence High School, on High Street, opened in September 1907, is yet another significant brick building in Fairfield (see the Oct. 7, 2021, issue of The Town Line). It is now Fairfield Primary School.
Main sources
Fairfield Historical Society, Fairfield, Maine 1788-1988 (1988.)
Grow, Mary M., China Maine Bicentennial History including 1984 revisions (1984).
Kingsbury, Henry D., ed., Illustrated History of Kennebec County Maine 1625-1892 (1892).
Lepage, Carolyn A., Michael E. Foley and Woodrow B. Thompson, Mining in Maine: Past, Present, and Future (1990) found on line.
Wiggin, Ruby Crosby, Albion on the Narrow Gauge (1964).



 As housing costs keep climbing across the country, more than 11 million Americans report being behind on rent payments, according to Surgo Ventures. Add in inflation and other economic uncertainties, and millions more are on the brink of falling behind or facing eviction.
As housing costs keep climbing across the country, more than 11 million Americans report being behind on rent payments, according to Surgo Ventures. Add in inflation and other economic uncertainties, and millions more are on the brink of falling behind or facing eviction.

 The
The 

 Spectrum Generations is offering an evidence-based class, “Savvy Caregiver,” via Zoom, Tuesdays 6:30 to 8:30 a.m., from July 19 to August 23.
Spectrum Generations is offering an evidence-based class, “Savvy Caregiver,” via Zoom, Tuesdays 6:30 to 8:30 a.m., from July 19 to August 23.