Up and down the Kennebec Valley: Sebasticook dams & Josiah Hayden
by Mary Grow
An on-line map of Winslow, Maine (which readers might find helpful), shows the Kennebec River, running roughly north-south, as the town’s western boundary. The Sebasticook River joins the Kennebec from the east about halfway between the town’s north and south lines.
Outlet Stream flows north across Winslow’s south boundary from Vassalboro and joins the Sebasticook a little east of the Sebasticook-Kennebec junction. The Nov. 30 issue of The Town Line described some of the dams on Vassalboro’s section of the stream. The 1869 inventory of dams and dam sites that was a main source for the Vassalboro list continued with another four dams and three dam sites in Winslow.
Henry Kingsbury, in his 1892 Kennebec County history, also listed dams along “this stream.” The similarity of owners’ names on the two lists convinced your writer that “this stream” was Outlet Stream.
To make correlating the two sources interesting, the 1869 inventory listed the dams going downstream; Kingsbury listed them going upstream. Your writer chose to continue downstream (north), starting with the dam closest to the Winslow-Vassalboro town line.
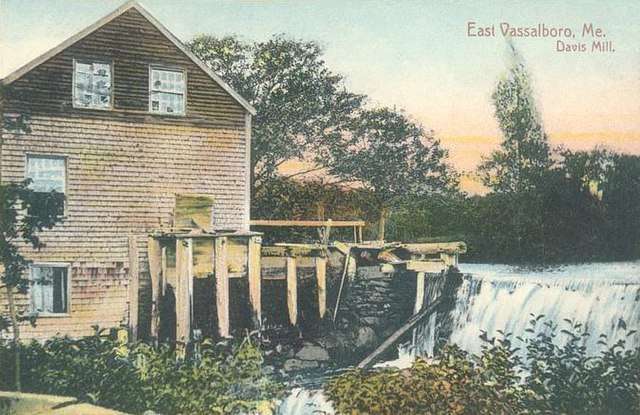
This was the seventh dam on the 1869 list, another 260 rods (a bit over eight-tenths of a mile) downstream from the last one in Vassalboro. Here T. S. and J. A. Lang, from Vassalboro, made knit goods and C. A. Priest made shoe pegs (the wooden pegs that attached shoe soles to the rest of the shoe).
(T. S. was Thomas Stackpole Lang, profiled in the Oct. 19 issue of The Town Line; he was born June 16, 1826, in North Berwick, and died June 18, 1895, in The Dalles, Oregon. J. A. Lang was his younger brother, John Alton Lang, born Jan. 27, 1840, in Berwick, and died Jan. 8, 1919, in Waterville.)
Kingsbury wrote that this dam initially powered a sawmill started by John Getchell in 1791 on the west bank, “where the woolen mill now [1892] is.” In the 1820s, Joseph Southwick and three Haydens, Howland, Pruden and Moses, organized a company that built a hemp mill on the east bank to provide local farmers with seed.
Hemp was used for fiber, especially to make sails and cordage for ships, and also bags, rope, clothing and similar items. Lesser uses included medicinal products and oil.
On-line sources list George Washington and Thomas Jefferson as hemp farmers. Principal production was in the southern states.
Hemp was not profitable in Maine in the 1820s, and Kingsbury wrote that around 1830, “Church and William Bassett, from Bridgewater, Mass., bought the property.” They “made shingles and barrel staves and put in carding machines.”
(A genealogy found on line says William Basset [March 27, 1777- Dec. 20, 1843] and his wife Abiah Williams [July 14, 1782-May 14, 1860] named their first two sons William Church Bassett and Williams Bassett. William C. was born April 4, 1803, in Bridgewater and died June 17, 1873, in Illinois; Williams was born April 1, 1806, and died Sept. 24, 1877, in Winslow, Maine.)
Kingsbury continued, “Church bought his brother out and started a woolen mill.” He sold part of the water rights to a man named Wilber, who made shingles. Bassett and Wilber each had a threshing machine, “and competition was brisk.”
In 1846, the sawmill burned, Kingsbury said. Five years later, Edmund Getchell and sons Ira and Leonard bought a quarter of the water rights on the west shore and “built a shop” where for 15 years they made shingles and did other wood-working, including “making large lots of spade handles for gold diggers’ use in California.”
John D. Lang (Thomas Lang’s father) and three Priest brothers, Henry W., Theodore W. and Charles A, bought the east side rights in 1857, Kingsbury said. They added a grist mill and converted the Bassett woolen mill into the shoe peg factory listed in 1869.
Kingsbury wrote that Charles A. Priest took over the latter, “inventing a machine for cutting shoe pegs that made him independent of a patent that had monopolized the cutting of these wooden nails for years.” He sold pegs as far away as Liverpool, England, “where one firm took 1,000 barrels of pegs a year at sixty cents a bushel.”
The mills on the east side of this Outlet Stream dam burned in 1865. The Priests sold the grist mill rights to John D. Lang, who rebuilt the mill. Kingsbury wrote that around 1880, Charles Priest and Charles A. Drummond bought it from Lang. (Lang died in 1879; perhaps Kingsbury meant from his estate.) It was still running in 1892.
Charles Priest rebuilt his shoe peg factory, but demand dwindled; by 1892 he was using the building for unspecified wood and iron work. In 1892, Kingsbury added, the shoddy mill Albert Cook built around 1880 was still in business, run by Cook & Jepson. (A shoddy mill reprocesses woolen rags into new cloth.)
On the 1869 list, the Langs owned the eighth dam, 60 rods (less than two-tenths of a mile) farther downstream, and in 1869 were planning to use it – a company had been chartered, with $100,000 capital. Kingsbury made no mention of development here, nor at what the list described as undeveloped sites for ninth and tenth dams.
Kingsbury discussed at some length the next site on the list, two miles downstream, where in 1869 T. J. Hayden ran a sawmill, threshing machine and other equipment on the 11th dam.
T. J. was Thomas Jefferson Hayden (Dec. 3, 1803-March 11, 1886), and Kingsbury said his mill was on the dam that his father, Major Josiah Hayden, built “nearly one hundred years ago,” or around 1792.
Your writer suspects “Major” is an error and the 1790s mill builder was young Josiah Hayden, Jr. There were two Josiah Haydens, father, born in 1734 and a Revolutionary veteran, and son, born in 1772 (see box). The son, Thomas Jefferson Hayden’s father, had no military record.
Josiah Hayden, Jr., started with a sawmill and in 1822 bought John Drummond’s grist mill (originally with two sets of millstones, but one was removed) and relocated it beside the sawmill.
After Thomas J. Hayden inherited the mills (his father died in 1827), he added a “grain thresher and separator” on the upper floor, which by 1892 had been replaced by newer ones. By then, Kingsbury said, the property had passed to W. Vinal Hayden (Aug. 22, 1839- 1916; son of Thomas and his wife, Clarissa [Houston] Hayden [Nov. 9, 1810-June 28, 1861]).
The Hayden dam backed up Outlet Stream to form Hayden mill pond, and Kingsbury wrote that the clay beside the pond was excellent for pottery. In the 1810s, he said, a potter named William Hussey and his partner, Ambrose Bruce, started a pottery on the dam that supplied earthenware to local households; Hussey’s milk pans were especially popular. (See the article on natural resources in the July 14, 2022, issue of The Town Line.)
According to the 1869 list, just below Hayden’s premises was a site for a 12th dam, where the river fell nine feet “with precipitous banks.”
The list says the 13th dam was another 120 rods, or a bit over a third of a mile, downstream, but Kingsbury’s next site was three-quarters of a mile distant. According to Kingsbury, this dam and mill were “probably” built by a family named Norcross before 1819.
Thomas Hayden’s brother, Franklin, owned the mill by 1840. He was trying to move it upstream on Election Day that year, and planning to get married that evening, when he fell and was killed.
In 1869, this dam was occupied by a sawmill and other facilities owned by Flye & Hayden – probably Thomas Hayden, as Kingsbury wrote that he succeeded his brother, and perhaps a descendant of an early settler named John Flye. The mill ran until around 1880. The compiler of the dam inventory commented, “Can take logs from the Sebasticook, which is but 40 rods [about an eighth of a mile] below.”
Kingsbury believed this Norcross/Hayden dam was neither the lowest nor oldest on Outlet Steam: here, as in Vassalboro, the Plymouth Company provided a sawmill and grist mill before 1770, to encourage settlement in the area.
Kingsbury wrote that a Revolutionary War veteran from Pownalboro, Benjamin Runnels, built the dam. In 1778, he moved to Winslow, where he was “a farmer, trader, lumberman and speculator, and a representative to the general court [the Massachusetts legislature].”
A man named David Garland who worked in the Norcross/Hayden mills in 1819 told Kingsbury there were “ruins of a double mill a few rods below.” Kingsbury concluded these were the remains of the Plymouth Company mills.
Benjamin Runnels has three on-line genealogies, none totally agreeing with any other.
He was born March 31, 1748 or 1749. He married at least once, to Hepzibah or Hepzinah Ayer or Bradley; one website adds Mary Demoranville as a second wife. He almost certainly had a son named John, perhaps born in 1771 in Pownalboro; there might have been another son, David, or daughters Rachel Emery and Mary Whitten.
Benjamin died June 22, 1802 or 1803, in Winslow.
Josiah Hayden Sr.
Different sources give Josiah Hayden, Sr., the title of captain, major or colonel, derived from his service in the America Revolution and, according to one source, the Winslow, Maine, local militia.
The on-line Find a Grave website says Hayden was born May 15, 1734, in Braintree, Massachusetts. In 1756 (Kingsbury says 1762), he married Silence Howard (Nov. 1, 1741 – Aug. 9, 1803), from Brockton.
When the Revolution started, he became a captain in the Braintree Minute Men; he served at Lexington in 1775. In the Sept. 16, 1776, Battle of Harlem Heights, he was the major commanding the 25th Massachusetts Regiment.
The Haydens had three sons, Charles (1764-1862), Josiah, Jr. (1772-1827), and Daniel (1782-1865) and four daughters, according to Find a Grave.
Kingsbury wrote that the Haydens moved to Winslow in 1789. However, Find a Grave says their youngest daughter, Mary, was born Oct. 22, 1780, in Bridgewater and youngest son, Daniel, was born in Winslow, suggesting the move north was in 1781 or 1782. (For reference, Winslow’s Fort Halifax dates from 1752, and the town, until 1802 including Waterville, was incorporated in 1771.)
In Winslow, Edwin Carey Whittemore’s history of Waterville includes records showing Hayden’s involvement with the land-owning Plymouth Company. He moderated an Oct. 10, 1787, meeting at which some of the company’s lots were distributed, and when company meetings moved to Winslow in 1803, Hayden became company clerk and treasurer, apparently until its final meeting in August 1806.
According to Kingsbury, Hayden was first elected Winslow selectman in 1791 and served for 10 years. He was town clerk from 1792 through 1795 and again in 1797.
Whittemore listed him as one of a seven-man committee appointed in February 1794 to oversee building a meeting house. In 1801, he served on the five-man committee that successfully petitioned the Massachusetts legislature to separate Winslow and Waterville. As the only selectman living on the east – Winslow – side of the Kennebec, he was authorized to call the first meeting in the truncated town.
Find a Grave says Hayden represented Winslow in the Massachusetts legislature; no date is given. He died in Winslow Sept. 2, 1818.
Josiah, Sr., and Silence, their three sons and younger daughters Elizabeth (1777-1860) and Mary (1780-1867) are buried in Winslow’s Howard cemetery. Oldest daughter Tiley (1766-1845) became Mrs. Jonathan Cary or Carey and is buried in Brockton, Massachusetts. Her next younger sister, Mehitable (1769-1829), became Mrs. Thomas Vose and is buried in Robbinston, Maine.
Main sources
Kingsbury, Henry D., ed., Illustrated History of Kennebec County Maine 1625-1892 (1892). Whittemore, Rev. Edwin Carey, Centennial History of Waterville 1802-1902 (1902).
Websites, miscellaneous.