Benton map
Continuing north on the east side of the Kennebec River, the next town after Winslow is Benton. Next north of Benton is Clinton.
These two towns share with Winslow not just the Kennebec, but the Sebasticook River as well. The Sebasticook meanders a bit west of south through Clinton’s town center, and past two of Benton’s once-four villages, on its way to join the Kennebec in Winslow.
Unlike Augusta, Vassalboro and Winslow, neither Benton nor Clinton ever included land on the west bank of the Kennebec.
Your writer intended to write about both towns this week. As usual, she found too much information; Clinton’s story will be postponed.
* * * * * *
What is now Benton began as the southern part of Clinton. It was part of the Kennebec Purchase. A summary history on the Town of Benton website says the area was surveyed in 1769.
The history section of Benton’s 2018 comprehensive plan names the earliest European settler as Ebenezer Heald, who in 1763 built the required cabin and cleared the necessary land to get a grant from Gershom Flagg. (Flagg was mentioned in the May 30 history article as a 1764 grantee on the west side of the Kennebec in Augusta.)
The first Benton settlers Henry Kingsbury listed in his Kennebec County history were Irish emigres George FitzGerald and David Gray, who settled on the Kennebec about a mile north of Benton Station. He gave no date, but said elsewhere the first settlers arrived in 1775, later than the Benton website and comprehensive plan say. Kingsbury named Flagg as an early settler on the Sebasticook around 1783, on a Plymouth Company grant that was “fifteen miles long by half a mile wide.”
It was not until 1842 that southern Clinton became a separate town. The Benton website credits the area that became Benton with the first sawmill on the Sebasticook, in 1773; the first doctor in town (Ezekiel Brown, Jr., at Benton Station on the Kennebec, in 1789); the first Clinton post office (at Flagg’s store in Benton Village on the Sebasticook, on July 29, 1811); and the first church building in town (the Congregational Meeting House at Benton Falls, also on the Sebasticook, in 1828).
Kingsbury wrote that Benton town records start with a March 16, 1842, Maine legislative act (Maine had become a separate state on March 15, 1820). This act divided Clinton and incorporated “the town of Sebasticook.”
A Historical Society slideshow on the Town of Clinton’s website illustrates the separation. It describes the line of demarcation beginning on the Kennebec, going east-southeast to the Sebasticook and up the middle of the Sebasticook to Clinton’s east boundary. It appears that Sebasticook took almost half Clinton’s land area.
Sebasticook, the comprehensive plan says, is an Anglicization of “Chebattiscook or Chebattis, meaning John Batstiste’s [Baptiste’s?] Place.” A Maine education website calls it a Penobscot word meaning “‘almost through place’ or ‘short passage river,’ referring to the short portage to the Souadabscook Stream, which connects the Penobscot and Kennebec rivers.”
At a March 4, 1850, town meeting, Kingsbury said, Sebasticook voters directed their selectmen to propose a new name. Selectmen chose Benton, which was approved by the legislature and first used at a September 1850 town meeting.
Sources your writer found are, for once, unanimous on the origin of the name: it honors Democratic U. S. Senator Thomas Hart Benton (March 14, 1782 – April 10, 1858). Benton served in the Senate from Aug. 10, 1821 to March 3, 1851; Wikipedia says he was the first person to serve five terms.
What else he was noted for depends on the source. Kingsbury mentioned only his 1854-1856 two-volume book, Thirty Years in the United States Senate (cited elsewhere as Thirty Years View).
Benton was a lieutenant colonel in the War of 1812, serving as Andrew Jackson’s aide, seeing no combat.
He fought several duels (an unlikely reason to name a town after him).
Wikipedia calls him “an architect and champion of [United States] westward expansion,” the movement also called Manifest Destiny.
He was a slave-owner, but opposed extending slavery into new territories.
The Encyclopedia Britannica says Benton insisted that public lands be distributed to people planning to settle on them; his political base in the 1820s was “small farmers and traders.”
Several sources mention Benton’s support of hard currency (“gold and silver coins instead of paper money and bank notes”), for which he was nicknamed “Old Bullion.”
It would be interesting to know which of these policies impressed the Benton selectmen, or what other choices, if any, they debated. Your writer notes two advantages of the new name: it’s closer to the top of alphabetical lists, and it’s shorter and quicker to say and write.
A Wikipedia article lists more than a dozen United States counties and towns named in Senator Benton’s honor, including Benton, Maine.
* * * * * *
Although Benton did not exist legally until March 16, 1842, Kingsbury and others begin their histories of the town decades earlier. Readers should remember that the name “Benton” in the following paragraphs is used retroactively until incorporation.
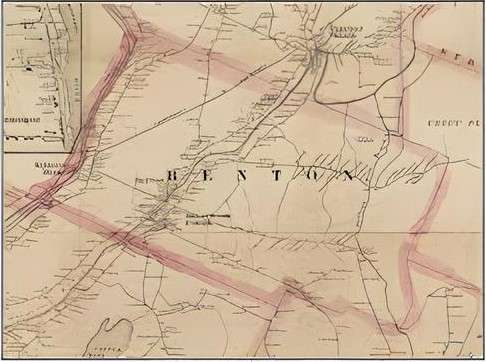
Kingsbury, finishing his history in 1892, named four villages in the Town of Benton: Benton Falls, Benton Village, East Benton and Benton Station (originally Brown’s Corner, where Dr. Brown settled). If these population centers began life as Clinton Falls, etc., your writer has found no historian who mentioned it.
Benton Falls and Benton Village were both on the Sebasticook, adjacent to waterfalls that provided water power. Benton Falls was and is on the east bank, on what is now Falls Road, running along the river from Route 139 south to the Winslow town line.
Your writer has been unable to find a definitive location for Benton Village, which no longer exists under that name. More intensive research in 19th-century land deeds should provide the information: Kingsbury identified the village, and other locations, by names of nearby pre-1892 residents.
There were two notable “falls” in the Sebasticook in the late 1700s and early 1800s, called upper falls and lower falls. Several sources, including Benton’s comprehensive plan and the town website, say Benton Falls was/is on the upper – upriver, or more northerly – falls.
The website lists, between 1769 and 1773, “First dam built at the upper falls (in now Benton Falls).” The plan says, “The first dam, erected at the upper falls in Benton Falls[,] was built before the Revolutionary War.”
Kingsbury, however, said the mills and shops at the upper falls were in Benton Village. He wrote that around 1800, Captain Andrew Richardson built an early sawmill on the east bank “at the upper falls (now Benton village).”
After much reading and map study, your writer sides with Kingsbury: as the Sebasticook flows toward the Kennebec, Benton (Village) is upriver, or north, of Benton Falls. This opinion is strengthened by the map in the 1879 Kennebec County atlas, which shows Benton P. O. (post office) on the west bank, upstream of Benton Falls P. O. on the east bank.
(The map in the 1856 atlas shows a densely populated area from south of Benton Falls to north of Benton Village on both sides of the Sebasticook and along roads paralleling it. This combined population center is labeled Sebasticook Corner on the east bank and Benton on the west bank.)
The present bridge where Route 139 crosses the Sebasticook, the Benton town office on the west bank a short distance downriver and nearby residences and commercial buildings are now in the area labeled Benton or Benton Village.
“Before 1800 a toll bridge was built and carried away several times by high water,” the Benton website says. Whether the river was bridged first at Benton Falls or Benton Village is unspecified. The 1856 map appears to show a bridge at each place.
East Benton and Benton Station are easier to locate.
East Benton was south of Fifteen Mile (or Fifteenmile) Stream, along today’s East Benton Road, in the southeastern part of town. Kingsbury listed two sawmills on Fifteen Mile Stream before 1840. They burned around 1855, were rebuilt and burned again sometime after 1870, he wrote.
The East Benton post office opened Aug. 5, 1858, Kingsbury said. The 1879 map shows an area labeled East Benton P. O. on the East Benton Road around the intersections with Richards, Hanscomb and Bog roads, on the west side of Fifteen Mile Stream.
On Dec. 28, 1887, Kingsbury said, the post office name was changed to Preston Corner; Daniel Preston had been postmaster since March 22 of that year, and served until Nov. 20, 1889. The name became East Benton again on May 29, 1891.
Benton Station was and is on the bank of the Kennebec, extending along the river both ways from the bridges between Benton and Fairfield. The 1879 map shows Maine Central railroad tracks through the village. The comprehensive plan says as of 2018, the former railbed was part of Benton’s Kennebec River Walking Trail.
Kingsbury said the first Benton Station post office was not established until May 31, 1878.
Going back to the Sebasticook, the comprehensive plan says a second dam was built at the lower falls in 1809, but it had no fish passage and therefore “so hindered the fishing that six years later the selectmen had it removed.” (But if the lower falls is really at Benton Falls, it must have been soon replaced to provide water power.)
The plan emphasizes the importance of fishing to early settlers, for food and as an “industry.” Main catches were alewives and shad; there were some salmon.
In 1817, the plan says, “fishing privileges were auctioned off so that sections of the river were sold to individuals.” Kingsbury added that people brought wagons from 40 miles around to collect fish, “which were thrown into the carts literally by the shovelful.” Alewives cost 25 cents per 100, shad four cents each.
The Sebasticook was a better fishery than the Kennebec because the Sebasticook was bridged and “could be spanned easily by weirs,” letting residents use both banks, the plan explained. The west bank of the Kennebec was and is in the Town of Fairfield.
Damming the Kennebec at Augusta in 1836 ended the fisheries.
Kingsbury said an early sawmill was built at the Sebasticook’s upper falls about 1800, and listed three mills and a tannery there in the 1820s.
Around the same time, he mentioned a blacksmith shop and Gershom Flagg’s grist mill at Benton Falls. Benton Falls, he said, had its first tavern by 1818, and by 1823 another tavern “where the pulp mill boarding house now [1892] stands.”
The comprehensive plan calls Benton Falls “the hub of the community” in the first half of the 19th century. The writer listed “at least three (3) sawmills, a tannery, carding and dye mill, grist mill and shingle mill.”
By the 1860s, “a brush and block-handle factory was run in the same building that wooden shoe sole shoes were manufactured. In 1872, a potato planter was invented and manufactured at the Benton Falls.”
The plan adds that Benton’s large pine trees were another economic resource. It says the masts for the USS Constitution (launched Oct. 21, 1797) were cut in Unity by a team of six men, mostly from Benton; hauled to the Sebasticook behind 20 oxen; and floated downriver through Benton.
Kingsbury listed early stores at Benton Falls (from 1808), Benton Station (from before 1810), Benton Village (from 1828) and East Benton (not until the 1870s). The East Benton store, “on the west corner of the road to Clinton,” began life as a smithy (no date), was enlarged and converted about 1878, and burned six days after it opened, he wrote.
The comprehensive plan says the “first frame house north of Augusta” was built on Benton’s Eames Road in 1772. (Eames Road runs southeast off Falls Road at the southern end of Benton Falls.) The builder’s name is omitted.
Main sources
Kingsbury, Henry D., ed., Illustrated History of Kennebec County Maine 1625-1892 (1892).
Town of Benton, 2018 Comprehensive Plan (found on line).
Websites, miscellaneous.
Correction and apology
For the article (above) on the Town of Benton, which was separated from Clinton in 1842, your writer reviewed multiple sources’ differing locations for the upper falls and the lower falls on the Sebasticook River.
She concluded the village of Benton Falls, on the east bank of the river, was founded at the lower falls. Having since had time to visit Clinton’s Brown Memorial Library and read part of Major General Carleton Edward Fisher’s admirably researched 1970 history of Clinton, she now believes she was wrong: Benton Falls, a mill village in the 19th century and a residential area today, was and is at the upper falls.
Fisher wrote that the lower falls were only about half a mile north of the Winslow town line. The upper falls were about half a mile farther upriver.
Another mile upriver, about where today’s highway bridge carries Route 139 across the Sebasticook a little north of the Benton town office, and where your writer erroneously located the upper falls, is what Fisher labeled Nine Mile Rips, a third stretch where the river drops comparatively rapidly.
The apology is to the writers of the Town of Benton’s website and comprehensive plan histories, who said, correctly, that Benton Falls was and is at the upper falls.













