Up and down the Kennebec Valley: Granges – Part 3
by Mary Grow
Palermo & Sidney
Palermo had two Granges for which multiple records exist, and Milton Dowe found an earlier third one in his research for his 1954 History Town of Palermo.
Dowe gives one paragraph to “Recreation Grange” – the quotation marks are his, and he did not add a number – in North Palermo, organized in 1875 and therefore among Maine’s first Granges. Dowe wrote that Leander Bowler owned the building where the Grange met, and that, “This grange did not exist many years.”
This writer has searched unsuccessfully on line for another reference to Recreation Grange.
Branch Mills Grange #336 started Jan. 1, 1897, and is included in the China bicentennial history (among other sources), though it has been headquartered in the Palermo side of Branch Mills Village most of its life. Sheepscot Lake Grange #445 was organized in 1905, in East Palermo.
The China history says Branch Mills Grange started with 20 charter members. Virginia Dowe, in a 1948 summary history included in Milton Dowe’s 1997 reminiscence, Palermo, Maine Things That I Remember in 1996, said there were 29 and named them. John Henry Barton, of Windsor, started the organization, at what the China history called the Good Templars Hall and Dowe called the “old Academy Hall.”
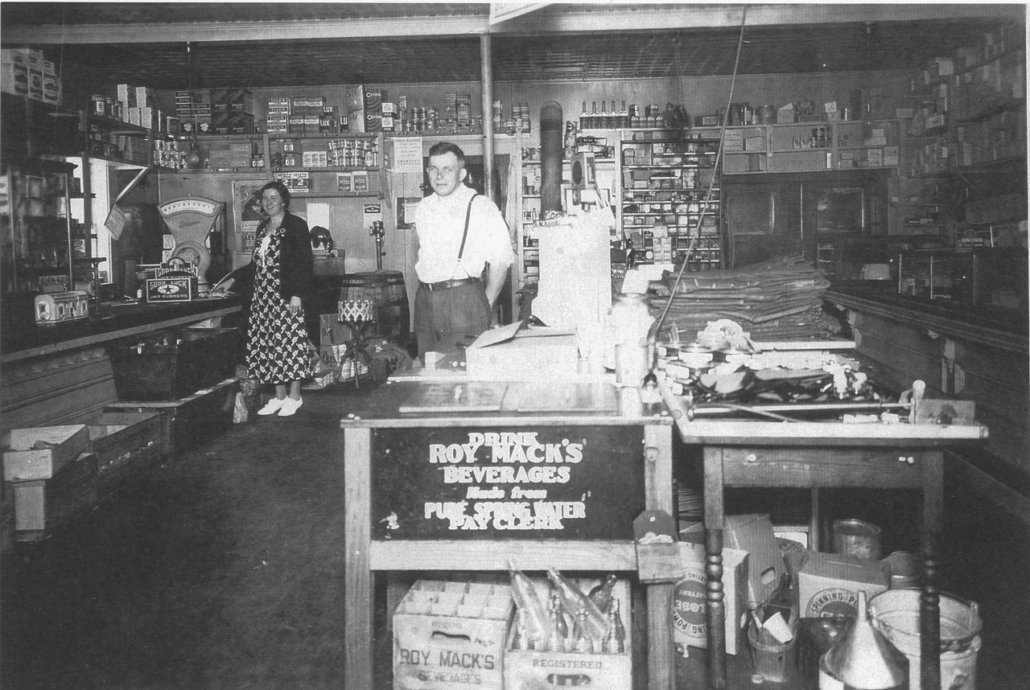
(Milton Edwin Dowe [Feb. 19, 1912 – Aug. 7, 2001] and Virginia Wescott Dowe [March 12, 1916 – Nov. 20, 2012] married April 29, 1939. They ran the Real Maine Country Store at the intersection of Branch Mills and North Palermo roads from the mid-1940s until 1981 or 1982. Among their many roles in the town, Milton Dowe helped organize the volunteer fire department and was its chief for 18 years, and Virginia Dowe was Palermo Town Clerk for 47 years.)
Kingsbury’s history says the first Good Templars group organized in Branch Mills lasted from December 1865 to sometime in 1869. In April 1874 it was succeeded by Lodge #349, which was still active in 1892. The Good Templars owned the building that Barzillai (or Brazillai) Harrington built for an academy in the mid-1800s.
Early 20th century records included two references to J. H. Barton, resident of West Windsor: he was a Windsor selectman in 1902, and he commented on the condition of orchards in a 1903 State Pomological Society publication.
The China history says that during its first year, Branch Mills Grange gained only 17 members, so in 1898 they organized a contest (unspecified) that brought 90 more people to join them. The larger group began planning to buy or build a Grange Hall.
By 1900, the China history says, they owned a former shoe shop in Branch Mills, on the west (China) side of the Sheepscot River. They enlarged and remodeled the building and held a dedication on March 13, 1902. That year, state Grange records say, there were 108 members.
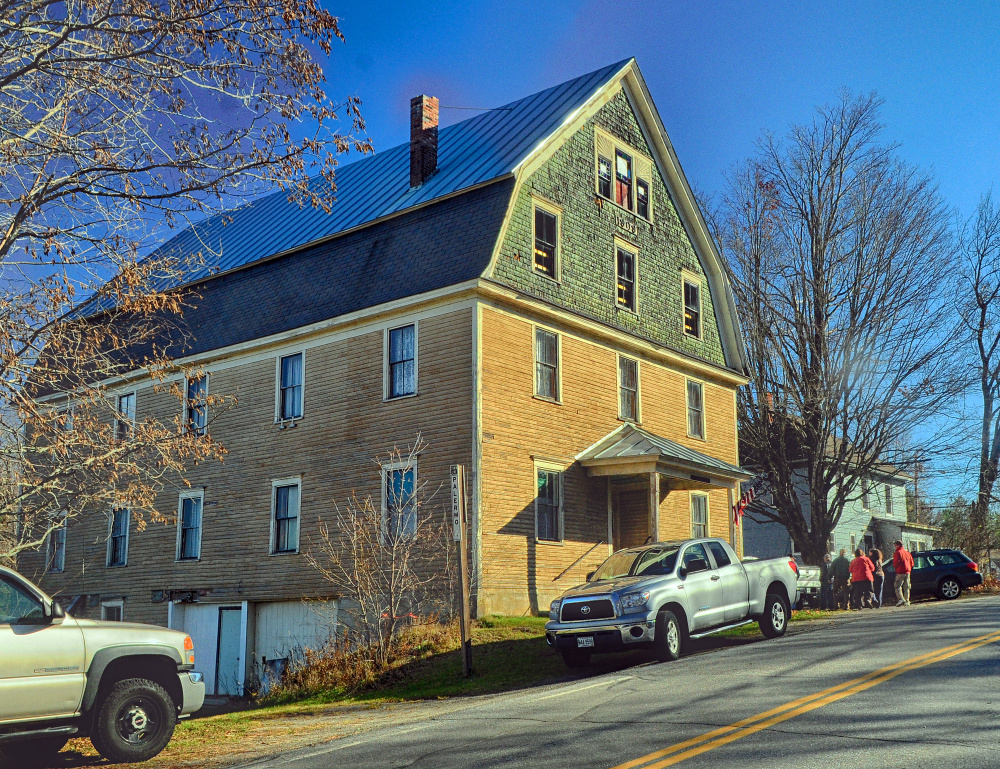
The Grange Hall burned in the June 26, 1908, fire that destroyed almost every building in the village. The China history describes what happened next, under the auspices of Eleon Shuman, at 18 “probably the youngest Grange Master in Maine,” and in 1975 a source of information for the history.
The Grangers sold their lot for $100, and for $300 bought a two-acre lot on the east (Palermo) side of the river from the Shuman family. They borrowed $4,000 and hired Fred Jordan as contractor.
Jordan in turn hired Shuman, who had been working as a painter for a man in China, and asked Shuman to do carpentry until it was time to paint. So Shuman “bought a saw and hammer and became a carpenter.”
Two jobs he remembered: nailing the rafters to the ridgepole, because “no one else wanted to climb that high”; and making the wooden figures 1909 and nailing them on the building’s face.
As in other towns, the Grange Hall served as a community center. For instance, Milton Dowe wrote in his 1954 history that when electricity reached Branch Mills in the summer of 1928, the lights were turned on on Aug. 8, and the Aug. 10 celebration was held in the Grange Hall.
The hall served as a meeting place for other town organizations. It hosted town meetings and other official public events. It was available for public entertainment, like dances, movies and plays; and for residents’ celebrations of weddings and the like.
Virginia Dowe wrote that during World War II Branch Mills Grange spent more than $500 helping and honoring soldiers. The Grange paid soldiers’ dues and sent Christmas gifts; and as veterans came home, Grange members gave each $25 and an honorary banquet.
In January 1947, Virginia Dowe continued, Grange members celebrated the organization’s 50th anniversary with “a tea, oyster stew supper and an old-fashioned dance,” with older members telling stories.
In the 1940s, she wrote, weekly dances in the winter provided funds for a furnace, installed in 1948.
Also in 1948, Milton Dowe wrote, Branch Mills Juvenile Grange #162 was established.
Grange-sponsored dances, “dramas” and other events benefited the volunteer fire department; Grangers donated $50 and let firefighters use the Grange Hall basement as a firehouse. The Grange Hall’s west wall was on the China-Palermo line and the basement door was on the west, so the fire trucks crossed into China as they left the building.
In 1949, Virginia Dowe wrote, Branch Mills Grange had 131 members and “a substantial fund in the treasury.” In 1975, according to the China history, the firefighters still occupied the basement and the Palermo town office was on the ground floor, leaving the second-floor meeting room for town meetings and Grange and other events.
Since 1975, a new town office and a new fire station have been built on North Palermo Road.
Branch Mills Grange was active in 2015 and is still listed as active by the Maine State Grange. The person listed on the state Grange website for information did not return a telephone call.
Sheepscot Lake Grange #445, in East Palermo, was organized Oct. 10, 1905, according to Milton Dowe’s history. Dowe wrote that its initial meetings were in the East Palermo schoolhouse, built by Paul Ames (who was related to novelist Ben Ames Williams).
Later, meetings moved to the second floor of Carroll Turner’s store. In 1907, Grange members bought a piece of land; in July 1907 the Grange was incorporated; and in the fall of 1908, members built a stable for their horses, presumably on the land they owned.
In 1907, Violet Lenfest reported to the state Department of Agriculture on behalf of Sheepscot Lake Grange. It was a bad year for insect pests. There were only a few “red-humped and yellow-necked apple worms,” fall webworms and grasshoppers; but cutworms, tent caterpillars, potato beetles, rose chafer beetles, “codling moths, cabbage worms, currant worms, railroad worms, horn flies and mosquitoes” were numerous.
Construction of the Sheepscot Lake Grange Hall started in the spring of 1910, and the building was finished in October. The first Sheepscot Lake Grange fair was held in the hall in September 1913; the fairs were still annual events when Dowe wrote in 1954.
Sheepscot Lake Juvenile Grange #106 “was chartered Feb. 15, 1941,” Dowe wrote.
In 1982, Sheepscot Lake Grange honored Walter Banton (Feb. 4, 1918 – Sept. 19, 2007), a World War II veteran active in town affairs, with its outstanding citizen award.
On the west side of the Kennebec, Sidney Grange #194 was organized Nov. 24, 1875, with 25 charter members. One of the members’ first actions, Alice Hammond wrote in her Sidney history, was to borrow $200 “to buy groceries to be sold to members at cost.” In 1876, they got a license to sell tobacco.
In 1885 Sidney Grange members started the Sidney Agricultural Fair, and from 1887 they invited non-members to bring entries. The fair was held annually at the town house on Middle Road. Kingsbury wrote that the Fair’s best displays were fruit and working cattle: “seventy-five yoke of the latter, driven in one continuous line, were shown one year.”
Brothers George and Frank Bowman had the largest tree nursery in Kennebec County, Kingsbury wrote. George Bowman was president of the Fair from 1887 until at least 1892 and was one of the early Grange Masters.
Hammond wrote that Grange members held their early meetings on the second floor of a store building on River Road. When they started considering building or buying a permanent home, enough Middle Road farmers were members that the group asked to share the town house for a year.
As the arrangement continued, the Grangers added a second story to the town house. The town office, a kitchen and a meeting room/dining room were on the first floor; the Grange used the upper floor for meetings and social events.
An old photo in Hammond’s history shows the front of the “town and grange hall,” an unadorned wooden rectangle with a generous front entrance and a ground-floor window on at least one side of the entrance (the photo is unclear). There are three windows on the second floor and two more above them under the sloping roof.
When Kingsbury’s history was published in 1892, Sidney Grange had 160 members and owned a “capacious hall.” In 1894, Grangers reached agreement with the congregation of the neighboring Universalist Church to build a horse shed on the church’s land, to be owned by the church and used by both groups.
State Grange records show 310 members in 1902 and 282 in 1906. The state records include a report from the Grange’s Deputy of West Kennebec County on his Oct. 30, 1902, inspection of Sidney Grange. He recorded 307 members with more applications coming in while he was there.
He commented: “Books well kept and dues well paid up. Young Master well qualified for his work.
Hammond wrote that Grange meetings were held every Thursday evening until 1946, when they decreased to two Thursdays a month.
The Grange was a source of information for farmers and a community center for everyone, Hammond wrote. Grange gatherings often featured meals; she wrote of “bills for eight gallons of oysters for a stew” and coffee brewed in a “copper wash boiler with a spigot soldered near the bottom.”
On May 6, 1937, after a Grange meeting, the building caught fire. Because of fog, the fire wasn’t spotted promptly; and the Oakland fire truck got stuck in Middle Road mud. The hall, the horse shed and the church all burned; firefighters were able to pour enough water on the safe to keep town records from being destroyed.
Voters at a special town meeting agreed to rebuild their town hall at about the same place and again with the Grangers, Hammond said. Waterville Savings Bank donated land southwest of the former building site; town and Grange committees worked together to assemble a building crew; and money was accumulated from insurance and multiple other sources to provide the $9,533.15 needed “without an appropriation from the town.”
Hammond wrote that Grange members and town voters approved in 1937 and 1938 an agreement for the “use, care and renting” of the building that was still in effect when her history was published in 1992. By then, Sidney Grange had fewer than 50 members.
The 2003 town comprehensive plan says Sidney owned its separate town office building and had a half interest in the Grange Hall, splitting expenses with the Grange.
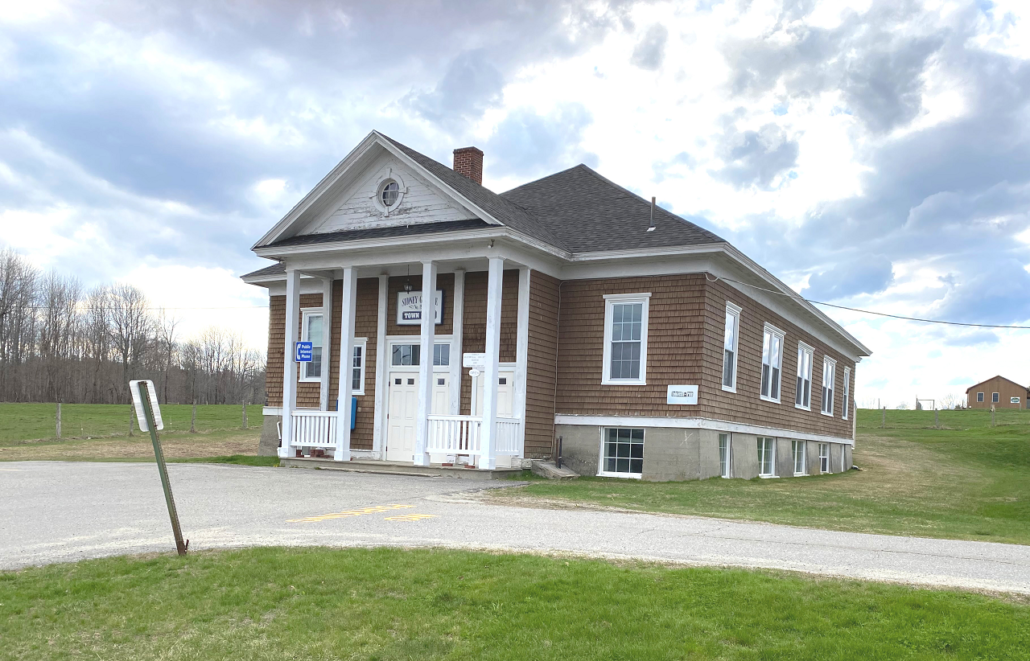
Currently the Grange Hall and the single-story town office building just north of it share a lot at 2986 Middle Road. The Grange Hall is a wood-shingled building atop a basement that rises above ground level. Across the center of the front, tall pillars support a pediment the height of the peaked roof, with a single window on each side on the basement and upper levels.
The Sidney Historical Society headquarters are in the basement. When this writer visited the hall recently, a sign on Middle Road advertised Young Americans Dance Center. A lady arriving with several young (elementary-school age) Americans said she believed dance classes were offered several days a week. YADC websites say the organization is based at Waterville’s Alfond Youth Center with a “secondary campus” in Sidney.
Main sources
Dowe, Milton E., History Town of Palermo Incorporated 1884 (1954).
Dowe, Milton E., Palermo, Maine Things That I Remember in 1996 (1997).
Grow, Mary M., China Maine Bicentennial History including 1984 revisions (1984).
Hammond, Alice, History of Sidney Maine 1792-1992 (1992).
Kingsbury, Henry D., ed., Illustrated History of Kennebec County Maine 1625-1892 (1892).
Websites, miscellaneous.